FIGURE 1.
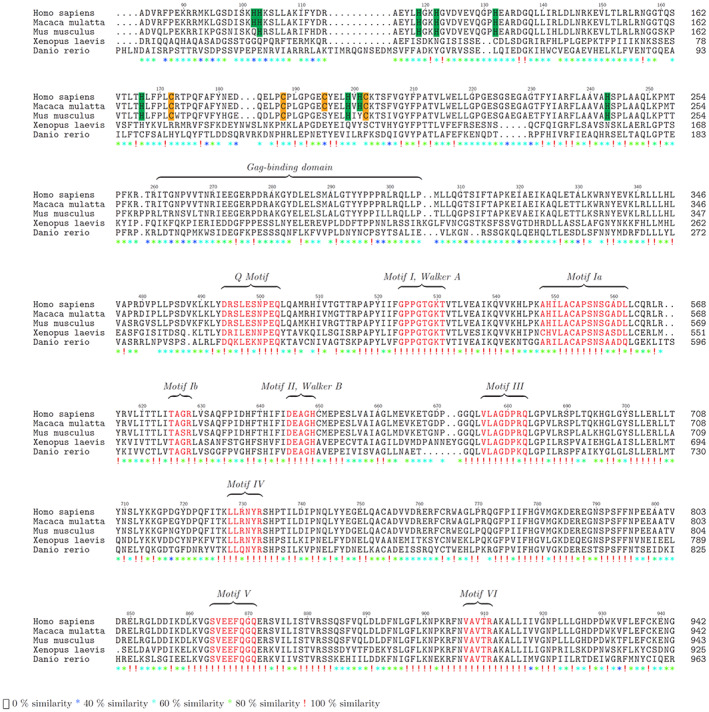
Evolutionary conservation of MOV10. Amino acid alignment of human (NM_020963.4), rhesus monkey (NM_001261223.1), mouse (NM_008619.2), Xenopus (XM_018246602.1), and zebrafish (NM_001044342.2) are shown beginning at amino acid 83 in Homo sapiens. The conserved cysteine and histidine residues between human, rhesus and mouse that form a consensus CH domain are highlighted in yellow and green, respectively. The helicase motifs are presented in red and annotated according to Fairman‐Williams et al. (2010), Rocak and Linder (2004), X. Wang et al. (2010). Gag‐binding domain is presented based on findings of Abudu et al. (2012). Red exclamation marks represent complete conservation across all five genera, green asterisks indicate strongly similar group conservation; asterisk of blue shades indicate weakly similar group conservation and blanks are regions of no conservation. Alignment was done using ClustalW function in msa package (Bodenhofer et al., 2015)
