FIGURE 5.
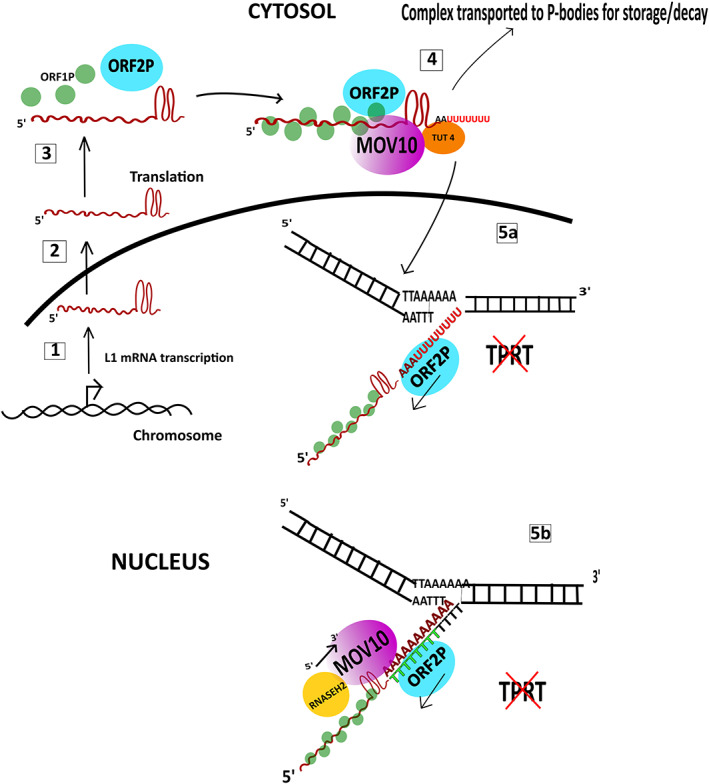
Proposed models for the role of MOV10 in inhibition of L1 retrotransposition: (1) L1 mRNA is transcribed by RNA polymerase and the transcript is exported to the cytosol. (2) The L1 mRNA is translated into ORF1P chaperone protein and ORF2P endonuclease/reverse transcriptase and assembled into the L1 RNP. (3) MOV10 binds at the rG4 present in the L1 3′ UTR. TUT4 binds MOV10 and adds U residues at the 3′ end. (4) The complex is taken to the PBs for storage or decay or exported back into the nucleus where L1 retrotransposition suppression is proposed to occur in two ways: (5) at the insertion site, the U residues are not complementary to the target site which results in failure of TPRT (Warkocki et al., 2018). (6) A second model proposed that at the site of insertion, ORF2p which binds to the polyA tail of the L1 mRNA attempts to reverse transcribe the L1 mRNA into cDNA and encounters steric hindrance from MOV10 which is moving in the 5′ to 3′ direction to unwind the rG4 or the DNA:RNA heteroduplexes in association with RNASEH2 (Choi et al., 2018; Skariah et al., 2017). TPRT, target‐primed reverse transcription; UTR, untranslated region
