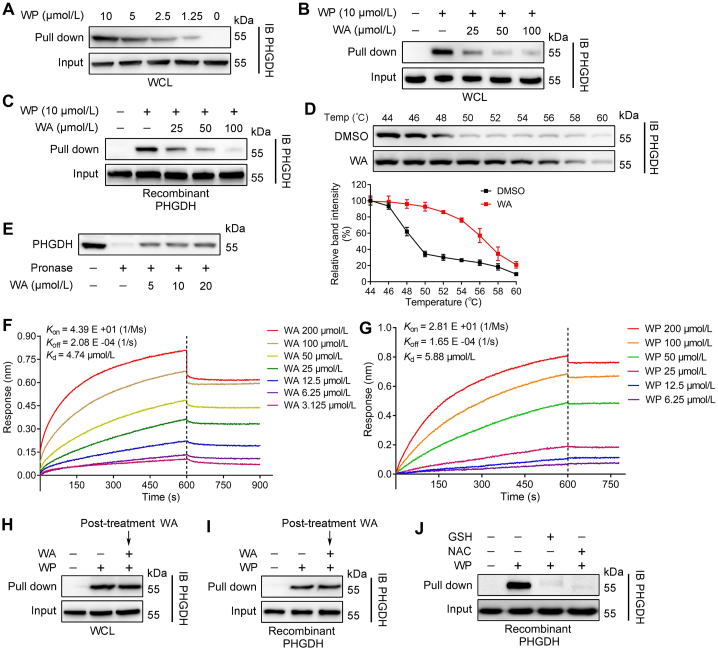
Figure 2.
WA directly binds to PHGDH. (A) Protein affinity pull-down assay was performed in HCT-116 cells by different concentrations of WP, and immunoblotting by PHGDH antibody. (B) Immunoblotting analysis of HCT-116 cells or (C) the recombinant PHGDH protein treated with WP in the absence or presence of WA for the competitive binding, and followed by protein affinity pull-down assay. The PHGDH bound to the WP were detected by immunoblotting. (D) CETSA assay was used to evaluate the binding between WA (5 μmol/L) and PHGDH in thermodynamic levels. The expression of PHGDH was detected by immunoblotting. Data are presented as the mean ± SD, n = 3. (E) HCT-116 cells lysates were treated with different concentrations of WA, and then incubated with pronase (5 μg/mL). The expression of PHGDH was detected by immunoblotting. (F) Interaction between WA and recombinant PHGDH protein was analysed by BLI assay. (G) Interaction between WP and recombinant PHGDH protein was analyzed by BLI assay. (H) HCT-116 cells were preincubated with WP (5 μmol/L) for 4 h and then further incubated with or without WA (50 μmol/L) for 2 h, then protein affinity pull-down assay was performed. (I) The recombinant PHGDH protein were preincubated with WP (5 μmol/L) for 2 h and then further incubated with or without WA (50 μmol/L) for 2 h, then protein affinity pull-down assay was performed. (J) WP was preincubated with glutathione (GSH, 1 mmol/L) and N-acetyl-cysteine (NAC, 1 mmol/L) for 2 h, then further incubated with recombinant PHGDH protein for 2 h, then protein affinity pull-down assay was performed.