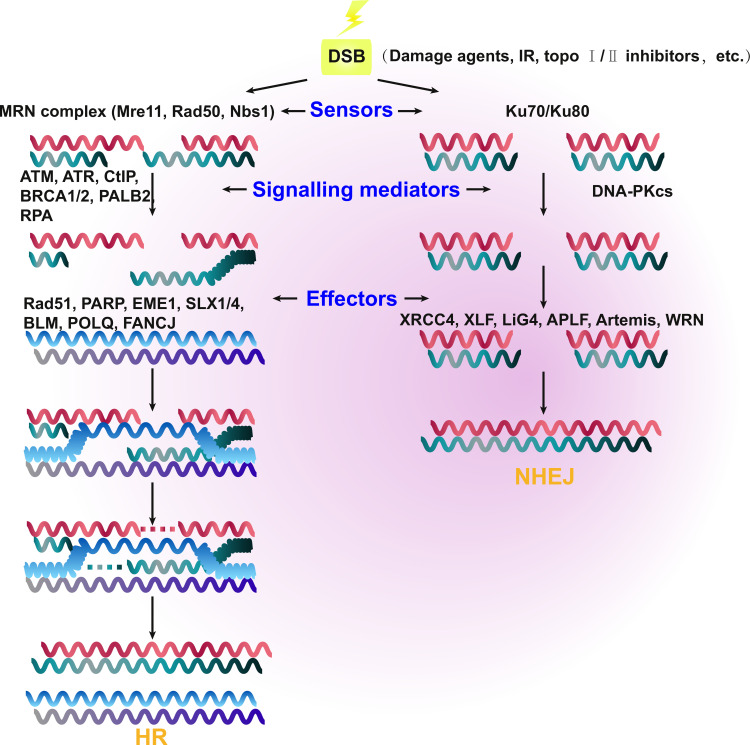
Figure 1.
Schematic representation showing the mechanisms of the two main double-strand break (DSB) repair pathways in cancer, namely homologous recombination (HR) and non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ). The relevant sensors recognize the region of damaged DNA and initiate the HR and NHEJ repair pathways. The MRE11–RAD50–NBS1 (MRN) complex and Ku70/Ku80 are the major sensor proteins. DNA DSB signals are mediated by various proteins, including ATM, ATR, CtIP, BRCA1, BRCA2, PALB2, and RPA in HR, as well as DNA-PKcs in NHEJ. There are also various effector proteins, which include Rad51, PARP, EME1, SLX1/4, BLM, POLQ, and FANCJ in HR, as well as XRCC4, XLF, LiG4, APLF, Artemis, and WRN in NHEJ.