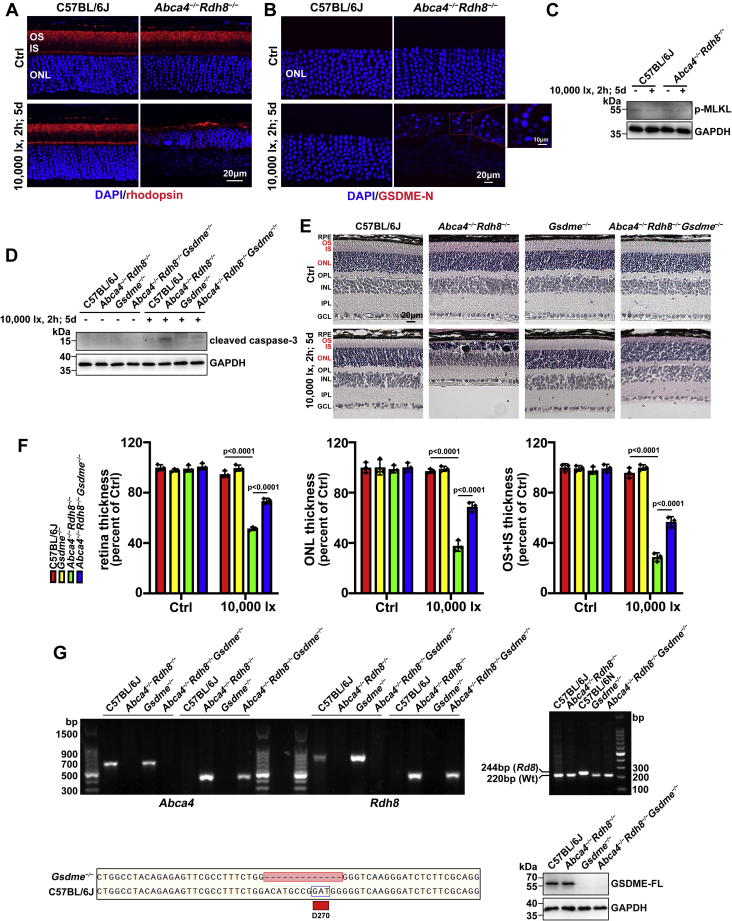
Figure 1.
Light-induced photoreceptor degeneration in Abca4−/−Rdh8−/−mice involves GSDME activation leading to pyroptosis and apoptosis, but it is unrelated to necroptosis. Four-week-old C57BL/6J WT, Abca4−/−Rdh8−/−, Gsdme−/−, and Abca4−/−Rdh8−/−Gsdme−/− mice were placed in a dark room for 2 days. After pupils of dark-adapted mice were dilated with 1% tropicamide, they were exposed to 10,000 lx light-emitting diode light for 2 h and then kept in the dark for 5 days. Control C57BL/6J WT, Abca4−/−Rdh8−/−, Gsdme−/−, and Abca4−/−Rdh8−/−Gsdme−/− mice were maintained normally in the dark for 7 days in the absence of light exposure. A, the morphology of photoreceptor OSs in mouse retina was evaluated by immunofluorescence staining for rhodopsin (red). Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). The scale bars represent 20 μm. B, protein levels of GSDME-N in photoreceptor ONL were determined by immunofluorescence staining of mouse retina with an anti-GSDME-N antibody (red). Nuclei were stained blue with DAPI. The scale bars represent 20 and 10 μm. C and D, immunoblotting was utilized to assess protein levels of p-MLKL and cleaved caspase-3 in extracts from neural retina. E, the histology of mouse retina was examined by H&E staining. The scale bars represent 20 μm. F, thickness of whole retina (F0.05 (3,16) = 153.1; p < 0.0001), ONL (F0.05 (3,16) = 83.28; p < 0.0001), or IS + OS (F0.05 (3,16) = 161.4; p < 0.0001) was quantified by Leica Application Suite X microscope software and expressed as a percentage of that measured in control C57BL/6J WT mice without exposure to light. Statistical analyses were performed by using two-way ANOVA with Tukey's post-test. G, genotyping of Abca4−/−Rdh8−/−, Gsdme−/−, and Abca4−/−Rdh8−/−Gsdme−/− mice with a C57BL/6J genetic background was performed by PCR amplification of tail DNAs with specific primers. In a previous report from our laboratory, we have shown a detailed textual description for PCR analysis of Abca4 and Rdh8 gene deletions and the absence of rd8 mutation in the Crb1 gene in mice (6). C57BL/6N mice carrying Rd8 mutation of the Crb1 gene served as a positive control. Diagrammatic representation of a part of gene sequence in the seventh exon of Gsdme that locates in chromosome 6 from C57BL/6J WT and Gsdme−/− mice. Compared with C57BL/6J WT mice, the sequence of the gene encoding GSDME in Gsdme−/− mice lacks 13 bp in which D270, the caspase-3 recognition motif, is included. Western blotting was used to analyze GSDME-FL expression in neural retina of C57BL/6J WT, Abca4−/−Rdh8−/−, Gsdme−/−, and Abca4−/−Rdh8−/−Gsdme−/− mice. GAPDH in C, D, and G was used as an internal control. Molecular mass markers (kilodalton) in C, D, and G were indicated to the left of immunoblots. Results in A–G are from at least three mice per group. DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; GCL, ganglion cell layer; GSDME, gasdermin E; GSDME-N, N-terminal fragment of GSDME; INL, inner nuclear layer; IPL, inner plexiform layer; IS, inner segment; p-MLKL, phosphorylated mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein; RPE, retinal pigment epithelium; ONL, outer nuclear layer; OPL, outer plexiform layer; OS, outer segment.