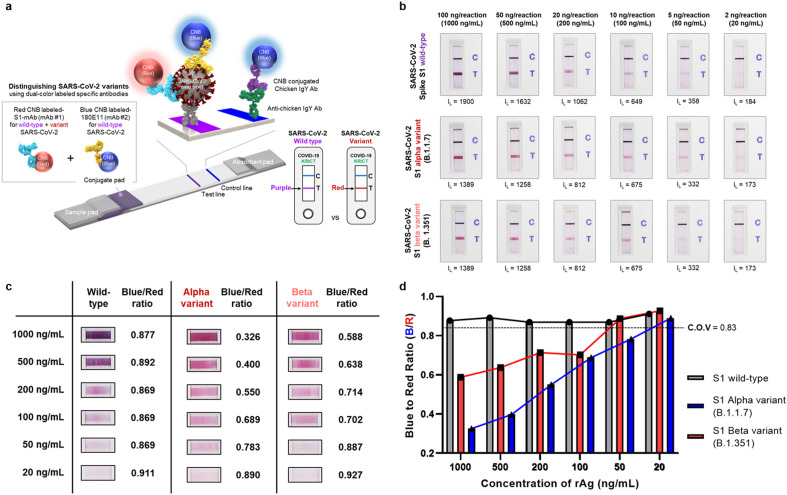
Fig. 4.
Distinguishing SARS-CoV-2 wild-type antigens from variant antigens. a) Schematic illustration showing the use of the ACE2-based biosensor to distinguish SARS-CoV-2 wild-type antigens from the variants. Two color-labeled SARS-CoV2-specific antibodies were co-deposited onto the conjugate pad. A specific antibody labeled with red CNB detects both wild-type S1 and the S1 variants; however, a second specific antibody labeled with blue CNB detects only wild-type S1. Therefore, the color of the test line depends on whether wild-type S1 (purple) or an S1 variant (red) is detected. b) The results of the tests. Performance was evaluated using SARS-CoV-2 S1 antigens (wild-type, alpha variant, and beta variant) serially diluted from 1000 ng/mL to 20 ng/mL c) Representative images of test lines and the blue-to-red ratios. At the reaction end-point (after 20 min), the test lines were analyzed using commercial software (ImageJ) to examine the RGB composition. d) Bar graph showing the blue-to-red ratio obtained from the serially diluted sample tests. The cut-off-value (C.O.V) was determined as the mean value of the blue-to-red ratio for the wild-type S1 minus three times the standard deviation.