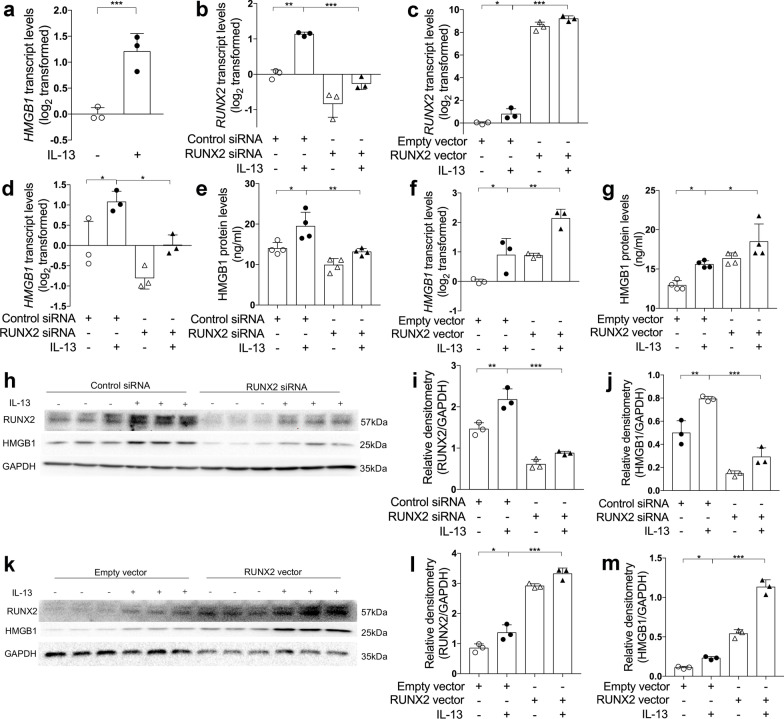
Fig. 5.
RUNX2 promotes HMGB1 expression in airway epithelial cells. a The transcript levels of miR-30a-3p in control and IL-13-stimulated BEAS-2B cells were determined by quantitative PCR. The transcript levels were expressed as log2 transformed and relative to the mean of control group (two-tailed Student’s t test). b–d, f The transcript levels of RUNX2 (b, c) and HMGB1 (d, f) after transfection with control or RUNX2 siRNA with or without IL‐13 stimulation, and empty or RUNX2 cDNA expression vector with or without IL‐13 stimulation were detected by quantitative PCR. The transcript levels were expressed as log2 transformed and relative to the mean of control group. e, g The protein levels of HMGB1 in cell culture media were determined by ELISA, after transfection with control or RUNX2 siRNA (e) with or without IL‐13 stimulation, and empty or RUNX2 cDNA expression vector (g) with or without IL‐13 stimulation. h–m The protein levels of RUNX2 and HMGB1 in BEAS-2B were determined by Western blotting after transfection with control or RUNX2 siRNA with or without IL‐13 stimulation (h–j), and empty or RUNX2 cDNA expression vector with or without IL‐13 stimulation (k–m). Densitometry assay of the Western blotting results was analyzed using ImageJ, and the protein levels of RUNX2 and HMGB1 were indexed to GAPDH. n = 3–4 wells per group. Data are mean ± SD. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 (one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test)