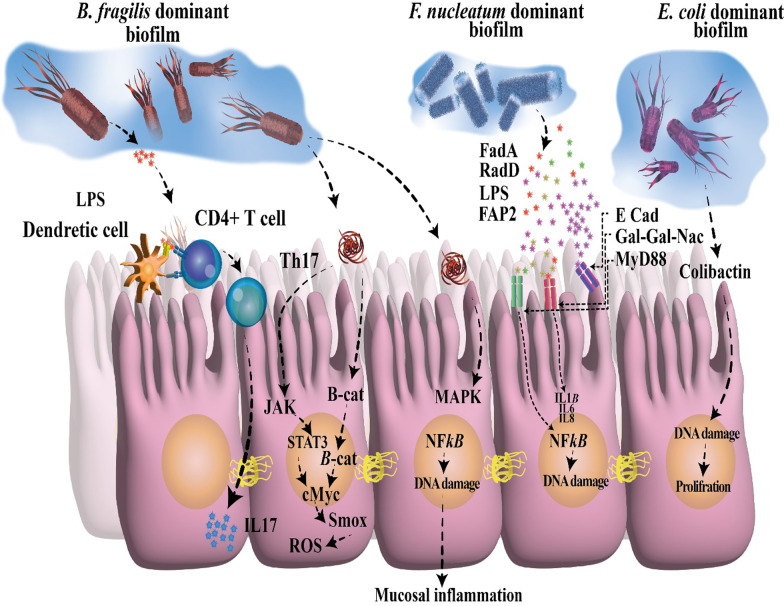
Fig. 1.
The polybacterial biofilm in colonic mucus. Bacterial biofilm can cause enhance the gut permeability, change of E-cadherin in colonic cells. Besides, biofilm can cause the loss of intestinal barrier activity, resulting in dysbiosis that could favor the enhanced growth of opportunistic pathogens. Eventually, the pro-oncogenic role of the biofilm and changes of polyamine metabolic and inflammation-associated Th17 prompt the growth of host cells, resulting in CRC initiation. CRC, colorectal cancer