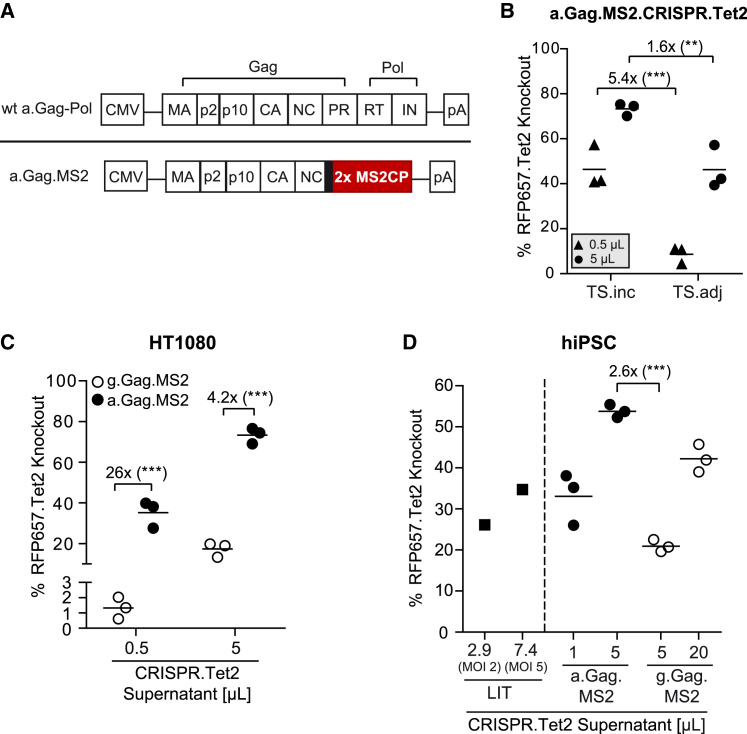
Figure 2.
Alpharetrovirus-based Gag.MS2 particles showed improved delivery of CRISPR-Cas9 components into target cells
(A) Design of alpharetroviral Gag.MS2 (a.Gag.MS2) variants. The wt alpharetroviral Gag-Pol polyprotein (wt a.Gag-Pol) is shown at the top of the figure panel. In contrast to g.Gag-Pol, alpharetroviral PR is part of the Gag open reading frame (ORF) (and not Pol ORF). In the depicted a.Gag.MS2 variant, the MS2CP dimer was separated from NC by the naturally occuring viral protease site (black bold bar). (B) a.Gag.MS2.CRISPR.Tet2 particles containing the Tet2.TS.inc sgRNA variant depict higher knockout rates compared with their Tet2.TS.adj counterparts. Indicated volumes of supernatants were used to transduce HT1080-based RFP657.Tet2 reporter cells. The graph depicts RFP657.Tet2 knockout rates mediated by three independent supernatants (n = 3). (C) a.Gag.MS2.CRISPR.Tet2 particles are superior to their gammaretroviral counterparts. Direct comparison of three individually produced a.Gag.MS2- and g.Gag.MS2-based CRISPR.Tet2 supernatants in HT1080-based RFP657.Tet2 reporter cells is shown (n = 3). (D) a.Gag.MS2.CRISPR.Tet2 particles mediate efficient targeted gene knockout in hiPSCs. hiPSC-based RFP657.Tet2 reporter cells were transduced with indicated volumes of three different batches of g.Gag.MS2.CRISPR.Tet2 or a.Gag.MS2.CRISPR.Tet2 supernatants (n = 3). A LIT.CRISPR.Tet2 supernatant applied at MOI 2 (2.9 μL) or MOI 5 (7.4 μL) served as a positive control (n = 1).