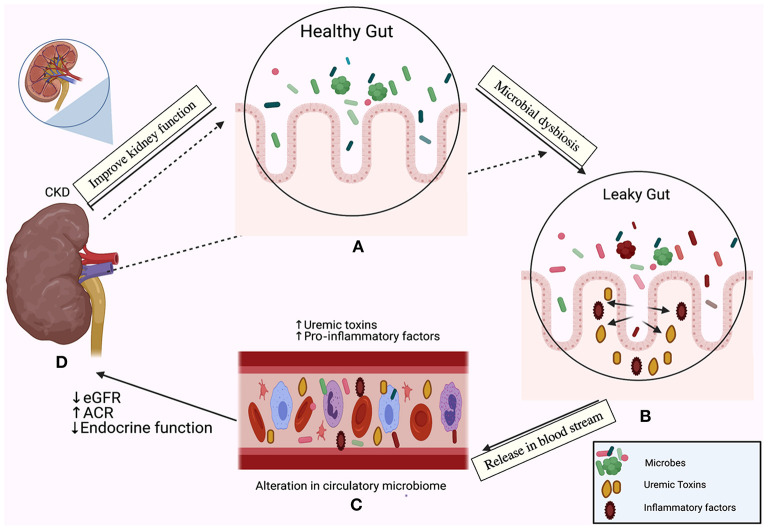
Figure 1.
The relationship between the gut microbiome and chronic kidney disease (CKD) is bi-directional. In one direction, the gut microbiota affect the kidney; the emerging role of gut microbiota in (A) The healthy gut, (B) The leaky gut due to microbial dysbiosis and disruption of the mucosal layer, (C) Release of pro-inflammatory factors in the bloodstream and initiation of the inflammatory cascade, accumulation of uremic toxins, (D) A decline in the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), the elevation of the albumin creatinine ratio (ACR) and loss of the endocrine functions of the kidney. In the other direction, CKD drives dysbiosis in the gut (indicated by the dotted arrows) and initiates an inflammatory cascade.