Figure 2.
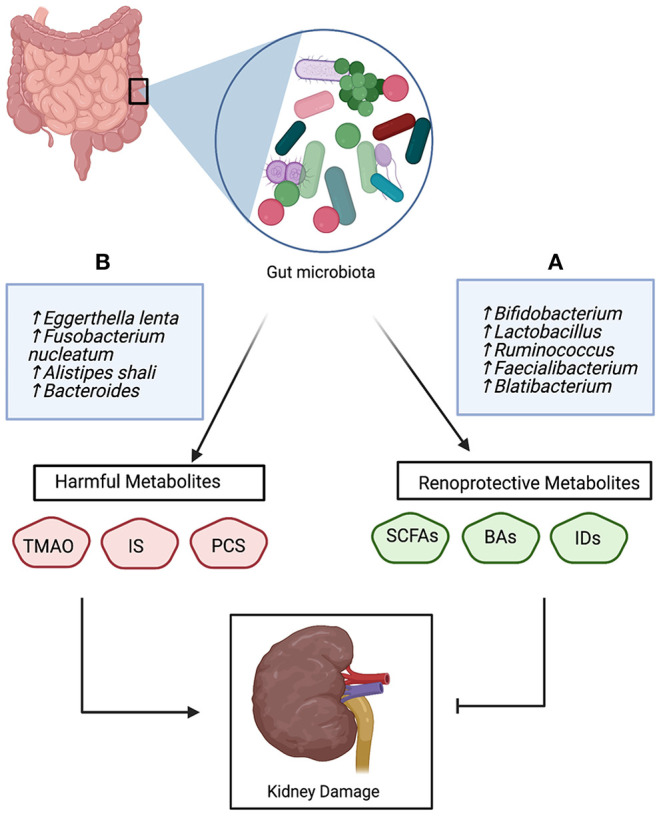
The bidirectional role of gut-derived metabolites in the pathophysiology of CKD; (A) Beneficial bacteria produce renoprotective metabolites that inhibit kidney damage, (B) Unfavorable bacteria produce harmful metabolites which promote kidney damage and CKD progression. Trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO), indoxyl sulfate (IS), p-cresyl sulfate (PSC), short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), bile acids (Bas), and Indole derivatives (IDs).
