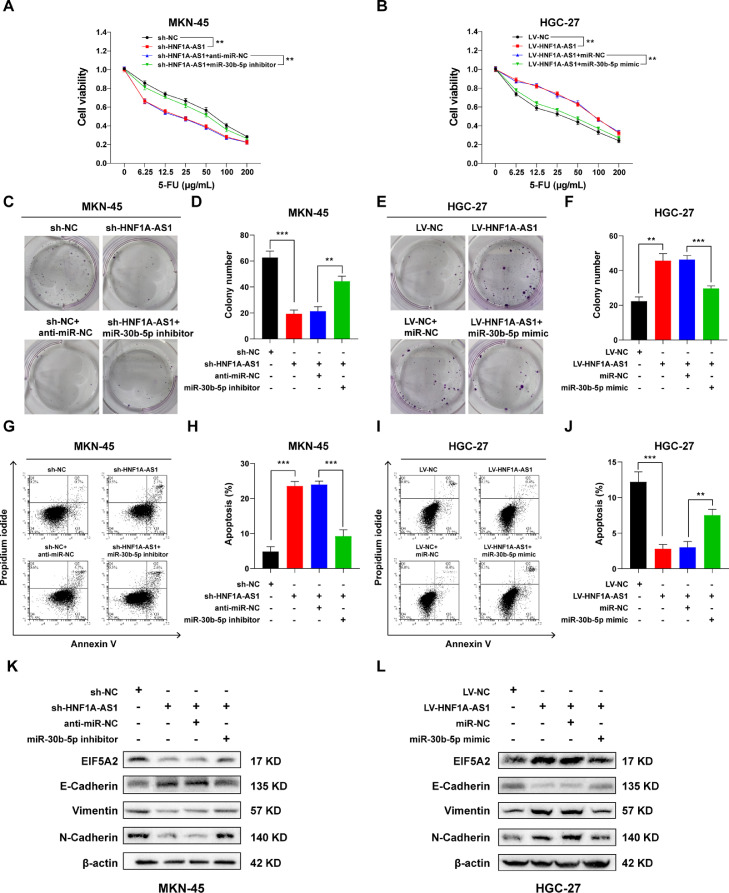
Fig. 5.
HNF1A-AS1 induced 5-FU resistance of GC cells through miR-30b-5p/EIF5A2 axis. (A) CCK-8 assay showed miR-30b-5p inhibitor reversed the suppressive effect of HNF1A-AS1 knockdown on cell viability of MKN-45 cells treated with 5-FU. (B) CCK-8 assay showed miR-30b-5p mimic reversed the promotion effect of HNF1A-AS1 overexpression on cell viability of HGC-27 cells treated with 5-FU. (C and D) The miR-30b-5p inhibitor reversed the suppressive effect of HNF1A-AS1 knockdown on colony formation of MKN-45 cells pretreated with 5-FU. (E and F) The miR-30b-5p mimic reversed the promotion effect of HNF1A-AS1 overexpression on colony formation of HGC-27 cells pretreated with 5-FU. (G and H) Flow cytometry showed miR-30b-5p inhibitor reversed the promotion effect of HNF1A-AS1 knockdown on apoptosis of MKN-45 cells treated with 5-FU. (I and J) Flow cytometry showed miR-30b-5p mimic reversed the suppressive effect of HNF1A-AS1 overexpression on apoptosis of HGC-27 cells treated with 5-FU. K Western blot showed HNF1A-AS1 knockdown downregulated EIF5A2, Vimentin, N-Cadherin protein expression and upregulated E-Cadherin protein expression, whereas miR-30b-5p inhibitor reversed these effects in MKN-45 cells. L Western blot showed HNF1A-AS1 overexpression upregulated EIF5A2, Vimentin, N-Cadherin protein expression and downregulated E-Cadherin protein expression, whereas miR-30b-5p mimic reversed these effects in HGC-27 cells. Data were presented as mean ± SD. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.