Figure 4. ADD1 variants disrupt protein functions.
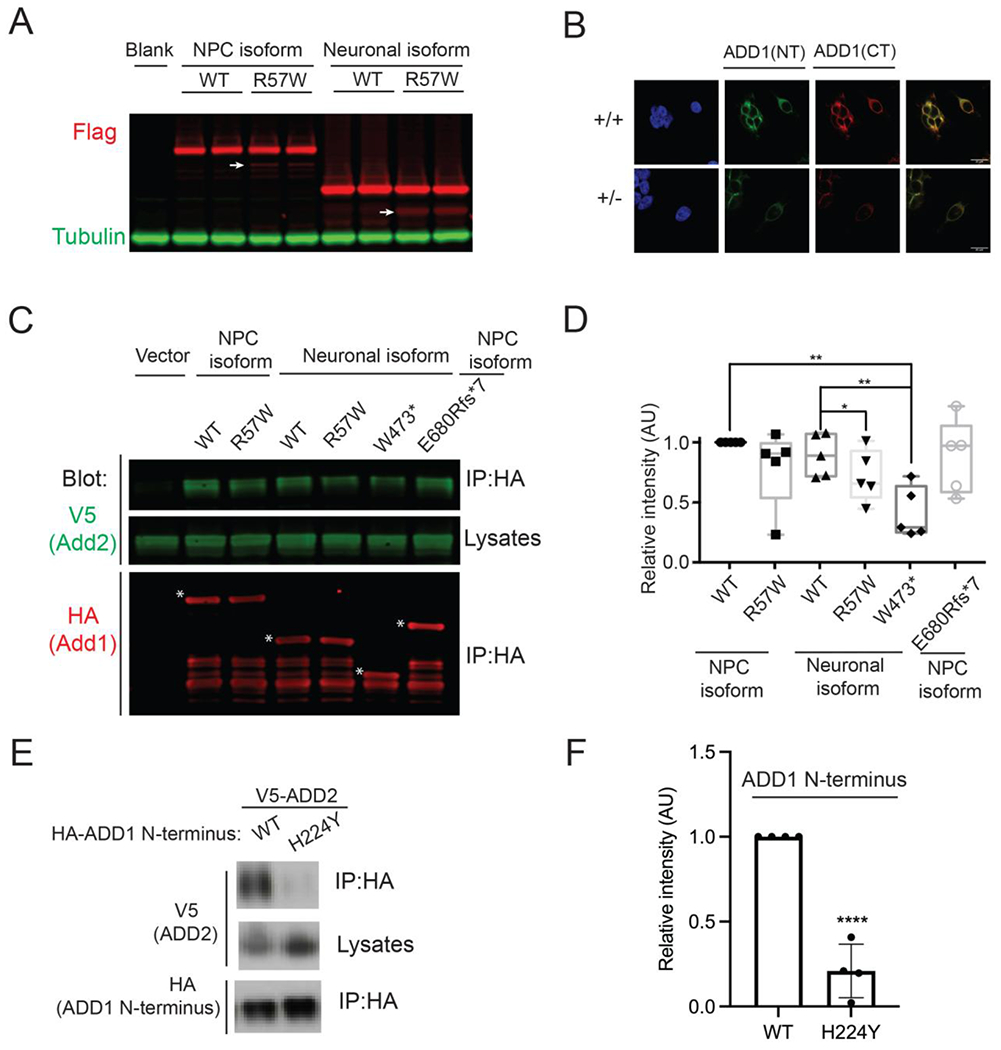
A) Expression of the ADD1 wildtype and mutant forms in Neuro2a cells showing that the Chr4:2877811 A>T (hg19, p.R57W) variant leads to a noticeable amount of truncated proteins (white arrows).
B) Immunostaining results using antibodies against ADD1 N terminal (ADD1(NT), green) and C terminal (ADD1(CT), red)) antibodies showing reduced protein level in ADD1 heterozygous (+/−) HEK293FT cells. Scale bar: 20μm.
C) Coimmunoprecipitation of V5-ADD2 transfected with indicated versions of HA-ADD1 (white stars) in HEK293FT cells, showing that ADD1 p.R57W and p.W473* reduced ADD1-ADD2 protein interaction.
D) Statistical analysis of signals in C) *P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, t-test.
E) Coimmunoprecipitation of V5-ADD2 transfected with indicated versions of HA tagged ADD1 N-terminus (1-430 amino acids) in Neuro2a cells showing that p.H224Y reduced ADD1-ADD2 protein interaction.
F) Statistical analysis of signals in E) ****P< 0.0001, t-test.
See also Figure S4.
