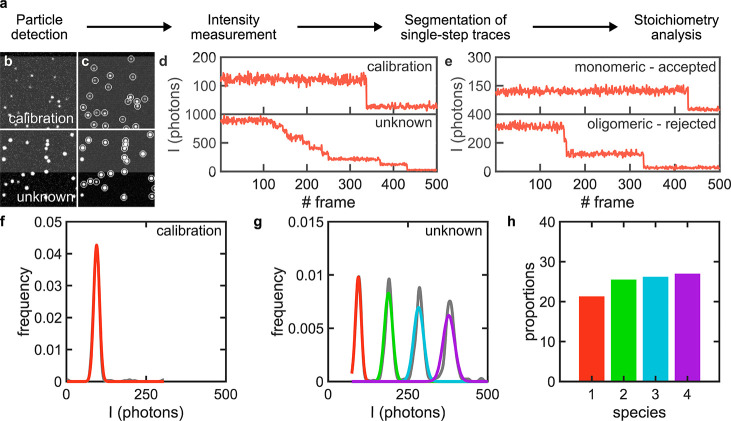
Figure 1.
Overview of the mode of operation of SAS. (a) SAS workflow. (b,c) Exemplary simulated, ground-truth images of single molecules for a set of calibration (stoichiometry: 50% monomers, 25% dimers, and 25% trimers) and unknown (stoichiometry: equal proportions of monomers to 16-mer) species (b) before detection and (c) after detection where detected particles are encircled with white circles. (d) Exemplary intensity traces of two randomly chosen particles from the calibration and unknown data sets after conversion from signal counts to photons. (e) Examples of monomeric and oligomeric traces extracted from the calibration data set that are automatically annotated by SAS. (f) Kernel density function of the intensity distribution underlying the calibration data set (gray) and the Gaussian curve representing the monomeric population (red). (g) Kernel density function of the intensity distribution underlying the unknown data set (gray) and the Gaussian mixture representing the monomeric population (red, green, cyan, and purple). (h) Bar graph of the proportion of the species underlying the unknown data set (color code as in panel g).