Figure 1: A schematic depiction of a Raman micro-spectroscopy instrument.
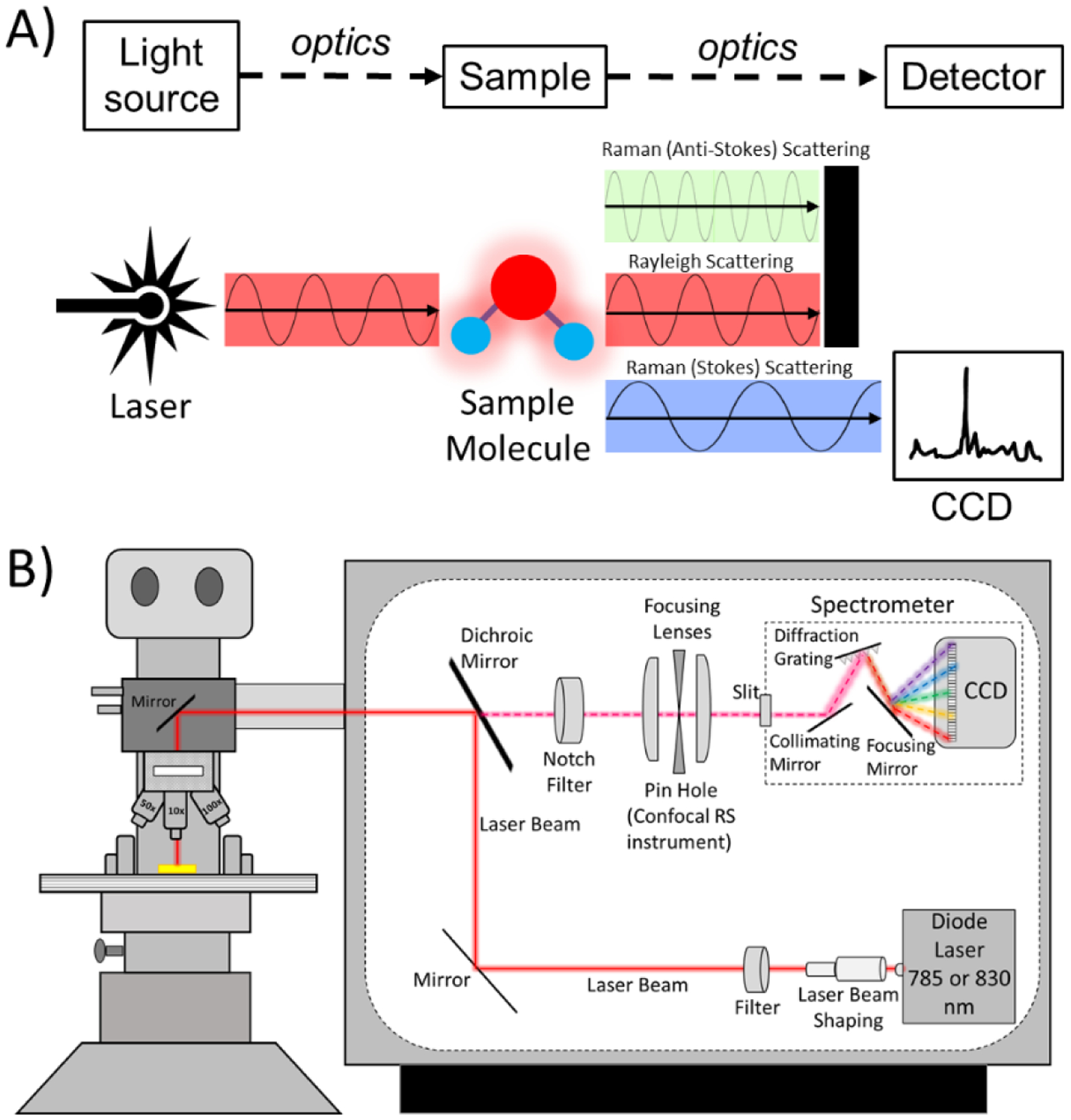
A) A Raman spectroscopy instrument has 4 primary components: a light source, a stage for the sample being analyzed, optics, and a detector. B) A commercial RS instrument includes mirrors, optical filters, focusing lenses, and objective lens to deliver the laser onto the sample and guide the collection of Raman scattered photons to the spectrometer (i.e., grating and detector, which is a charged-coupled device or CCD). The grating separates photons according to their wavelength in space so that the pixels of the CCD captures their intensity. Raman micro-spectroscopy has a confocality option which is provided by a pin hole aperture and slit. The optics of Raman micro-spectroscopy can preserve the polarization axis of the laser.
