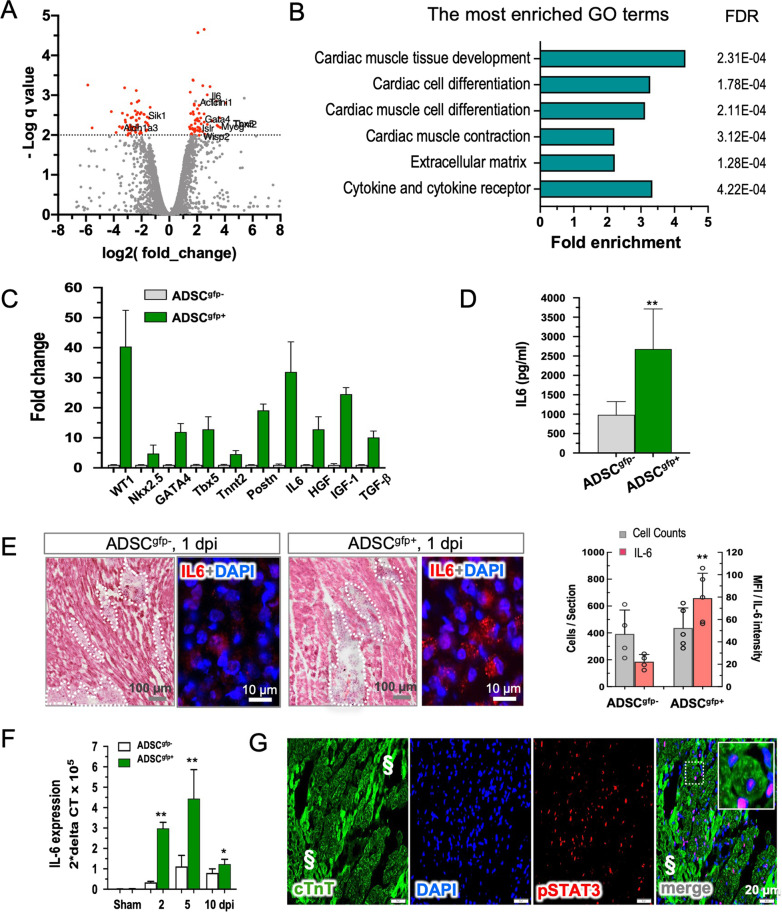
Fig. 3.
Identification of IL-6 as the most abundant cytokines secreted by ADSCgfp+. A Volcano plotting of bulk RNA-seq data illustrated a panel of differential expression genes between ADSCgfp+ (n = 3) and ADSCgfp− subpopulations (n = 3). B Gene ontology analysis categorized the up-regulated genes into GO-enriched terms related to cardiac differentiation and cardiogenesis, extracellular matrix formation and cytokine release. C RT-PCR analysis confirmed the upregulation of the selected genes from RNA-seq analysis. The mean expression level of ADSCgfp− was set as factor 1 (n = 5). Note striking up-regulation of WT1 and IL-6 expression in ADSCgfp+ subpopulation (n = 6). D Secretion of IL-6 was found significantly abundant in culture medium of ADSCgfp+ subset in comparison to ADSCgfp− subset (ELISA, n = 4, 5). E H&E staining was used to define the interstitial location of the injected cells in the host tissue, and immunodetection to compare the expression level of IL-6 in the injected cells at the early stage (1 dpi, left). Quantitative analysis revealed that both types of cells (ADSCgfp+ vs. ADSCgfp+) yielded identical cardiac retention (p > 0.05), but significantly high mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of IL-6 staining in the ADSCgfp+ subset (p < 0.01, n = 5 and 5, right). F RT-PCR detection of IL-6 expression in the cardiac tissue demonstrated a transient increase in IL-6 expression, peaking at 5 dpi. Remarkably, in the ADSCgfp+-injected hearts (n = 5) IL-6 expression was found significantly higher at all time points in comparison to ADSCgfp−-treated hearts (n = 4). G An important downstream nuclear target of IL-6, pSTAT3, was found to be activated exclusively in the viable cardiomyocytes after the treatment with ADSCgfp+ subset. § indicated dead myocardium (characterized by stark autofluorescent background in immunostaining). *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01