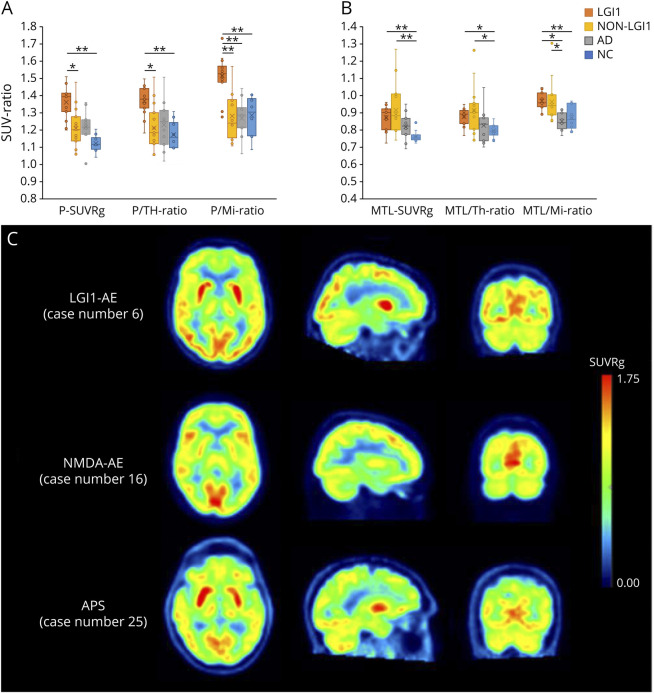
Figure 1. Regional [18F]FDG-PET Findings in LGI1- and Non–LGI1 AE Groups, Alzheimer Disease Group, and NCs.
Metabolic activity in (A) putamen and (B) MTL, measured as standardized uptake value ratios (SUVR) normalized to global brain, thalamus and midbrain. (C) Visualization of metabolic abnormalities in individual patients in LGI1-AE and non–LGI1-AE groups using parametric, global normalized [18F]FDG SUVR images. The images represent patients with LGI1-AE (case 6), NMDAr (case 16), and APS-associated (case 25) autoimmune encephalitides (AE) and demonstrate putaminal hypermetabolism and relative occipital hypermetabolism in LGI1-AE, lateral occipital hypometabolism and normal putaminal metabolism in NMDAr-AE, and pronounced putaminal hypermetabolism in APS-AE. Numbering of the patient cases refers to the case numbers in Tables 1 and 2. *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 (significant at the level of p < 0.05). [18F]FDG = [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose; AD = Alzheimer disease; AE = autoimmune encephalitis; APS = antiphospholipid syndrome; LGI1 = leucine-rich, glioma–inactivated-1; Mi = midbrain; MTL = mediotemporal lobe; NC = negative control; Non-LGI1 = non-LGI1 autoimmune encephalitis; P = putamen; SUV = standardized uptake value; SUVRg = global brain normalized standardized uptake value ratio; Th = thalamus.