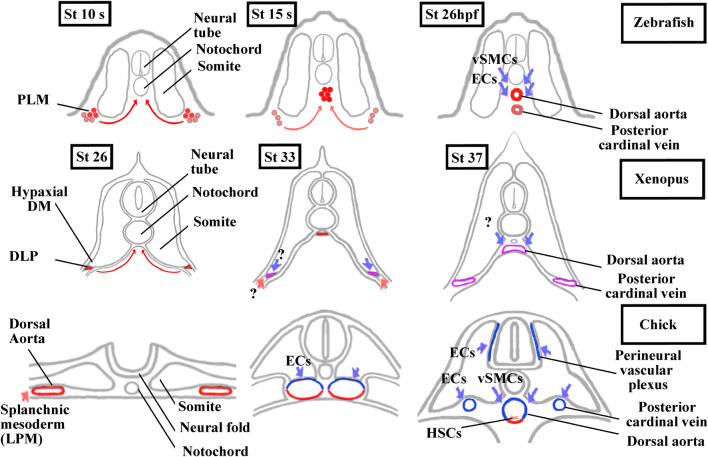
FIGURE 6.
Comparison of aorta and posterior cardinal vein formation and their somitic contributions between zebrafish, Xenopus, and chick. The ECs and vSMCs that make up the blood vessels throughout the body have various origins. While ECs are exclusively from the splanchnic or the somitic mesoderm, vSMCs are derived from the neural crest and, from the splanchnic or the somitic mesoderm (Pardanaud et al., 1996; Pouget et al., 2006 and, 2008; Etchevers et al., 2001). The aorta formation has also been the focus of intense research in vertebrates as the adult hematopoietic stem cells are generated from the ventral aortic hemangioblasts. This bipotent progenitors can also differentiate into endothelial cells (Pardanaud et al., 1996; Pardanaud and Dieterlen-Lièvre, 1999; Ciau-Uitz et al., 2010; Ciau-Uitz and Patient, 2016). In zebrafish, the aorta hemangioblasts are the first to migrate from the PLM to the midline, coalesce, and form the single aorta. A distinct population of endothelial cells migrates later from the PLM to the midline to form the posterior cardinal vein. ECs and vSMCs from the somites contribute to the aorta and probably to the posterior cardinal vein maturation. Modified from Kohli et al. (2013) and Hogan and Schulte-Merker (2017). In Xenopus, a single aorta is also made up of migrating hemangioblasts from DLP, whereas a pair of bilateral cardinal veins appears at trunk level. Until now, the somitic contributions to the aorta and bilateral cardinal veins are unknown. Modified from Cleaver and Krieg, (1998), Ciau-Uitz et al. (2000), and Charpentier et al. (2015). In chick, a pair of bilateral aorta is first formed from the lateral plate mesoderm before fusing at the midline and receiving ECs and vSMCs from the somites. The bilateral posterior cardinal veins are formed of ECs from the somites. The endotome remains difficult to characterize in amniotes since it seems that ECs derive from several somitic regions (Wilting et al., 1995; Nimmagadda et al., 2005). Modified from Sato, (2013) and Jaffredo et al. (2013). In red, lateral plate mesoderm derived cells. In blue, somite-derived cells. In purple, unknown origin. DLP, dorsal lateral plate mesoderm; DM, dermomyotome; ECs endothelial cells; HSCs, hematopoietic stem cells; LMP, lateral plate mesoderm; PLM, posterior lateral plate mesoderm; vSMCs, vascular smooth muscle cells.