Figure 1.
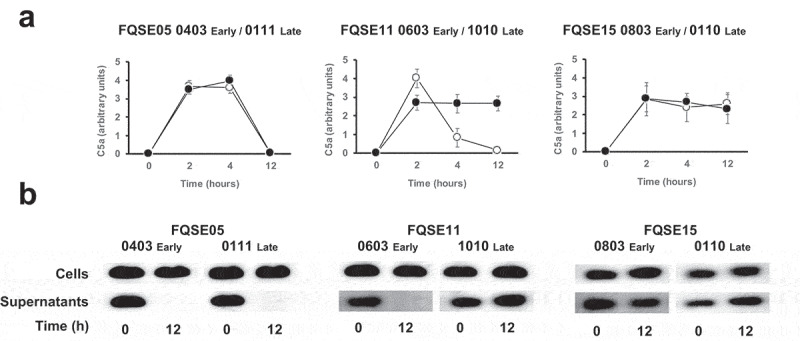
Analysis of the production and cleavage of C5a by P. aeruginosa strains isolated from CF patients with chronic airway infections. (a). Bacterial cells from three pairs of clonally related isolates, including the earliest (early, white circles) and the latest (late, black circles) isolate, recovered from three chronically infected CF patients were incubated in human serum (10%) and the amount of C5a produced was determined at different times by Western blot using a monoclonal antibody that recognizes C5a. Quantification of the C5a band was carried out by densitometric analysis. Results are the mean values and the standard deviation obtained from three independent experiments for each strain. (b) Purified recombinant human C5a (20 ng) was incubated for 1 h at 37°C with the cells or the cell-free supernatant from stationary cultures of P. aeruginosa strains isolated from CF patients with chronic airway infections. Proteins were separated and subjected to a Western blot with a monoclonal antibody that recognizes C5a.
