Figure 3.
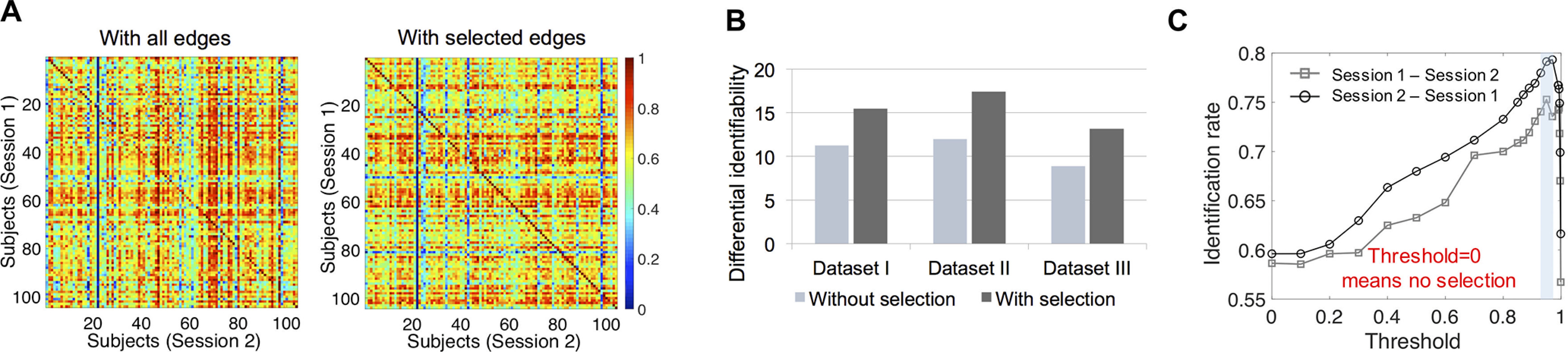
The importance of feature selection in the identification test of infants. A, The 104 × 104 cross-subject similarity matrices based on whole-brain edges and the selected edges thresholded at the 95th percentile of the SD values (Dataset II). Session 2 (S2) was acquired later than session 1 (S1). All the elements in the similarity matrices have been normalized by the maximum of each row. B, The average differential identifiability of corresponding cross-subject similarity matrices obtained with whole-brain edges and the selected edges thresholded at the 95th percentile of the SD values (Datasets I–III). C, The effect of the threshold for feature selection on identification accuracy. After the differential capability of the edges was ranked according to their SD across subjects, different thresholds of percentiles determine the edges retained for further identification. The shaded area represents the optimal area of the identification rate. In experiments, the threshold for each fold was determined by its performance on the training set.
