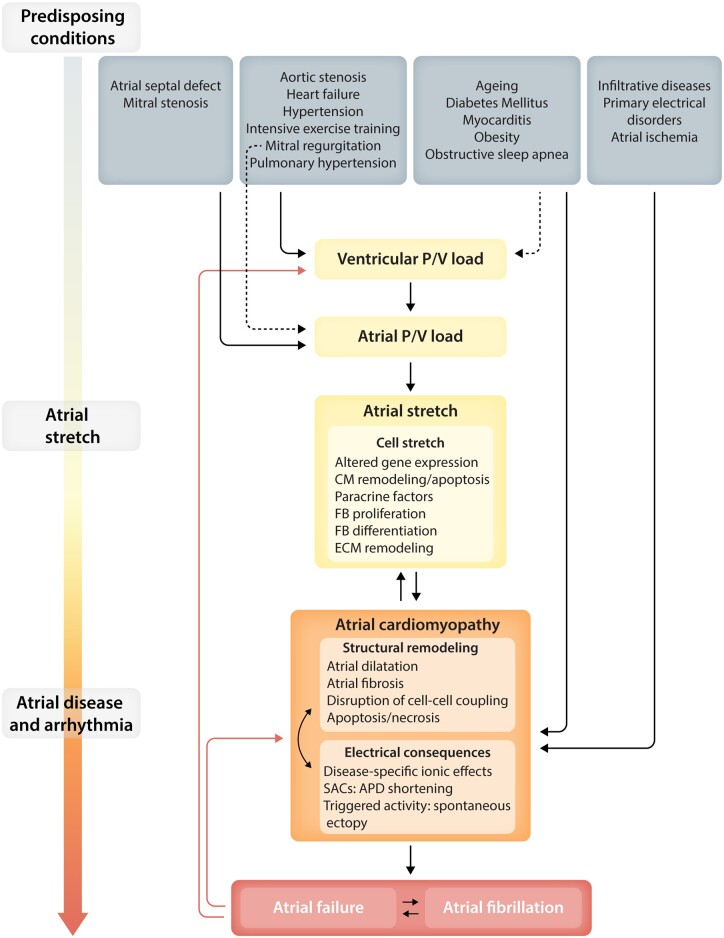
Figure 1.
Schematic of processes believed to be involved in AF-promoting responses to stretch. Conditions leading to atrial stretch and its consequences are shown at the top. These lead to atrial stretch, either directly via altered atrial load (primary or secondary to ventricular overload) or indirectly by affecting atrial function and causing atrial cardiomyopathy. Atrial stretch in itself causes cellular consequences that lead to atrial cardiomyopathy. Atrial cardiomyopathy leads to AF and can impair atrial function sufficiently to lead to atrial failure. CM, cardiomyocyte; ECM, extracellular matrix; FB, fibroblast; P/V, pressure/volume; SAC, stretch-activated channel.