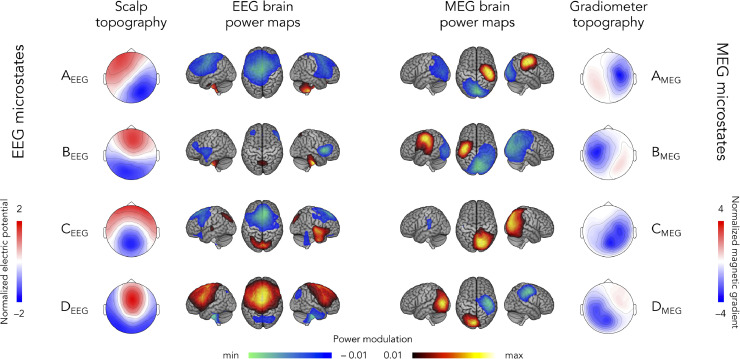
Fig. 3.
Spatial signature of EEG (left) and MEG (right) microstates. The scalp topography of EEG microstates (four-cluster AAHC of the 40 Hz-downsampled sensor maps at time points of local GFP maxima) is shown on the far left and the corresponding brain power maps on the middle left. The gradiometer topography of MEG microstates is shown on the far right and the corresponding brain power maps on the middle right. Scales for sensor-level topographical maps and source-level brain power maps are shown using different colors to emphasize their difference. The scales for sensor topographies correspond to electric potential (EEG) or magnetic gradient (MEG) distributions of each microstate normalized to their GFP. Positive (negative) values in the brain power maps indicate increasing (decreasing) power upon microstate activation. The scale of these brain power maps represents partial correlation values which were thresholded statistically, and the lower/upper limits are adapted to the minimum/maximum values.