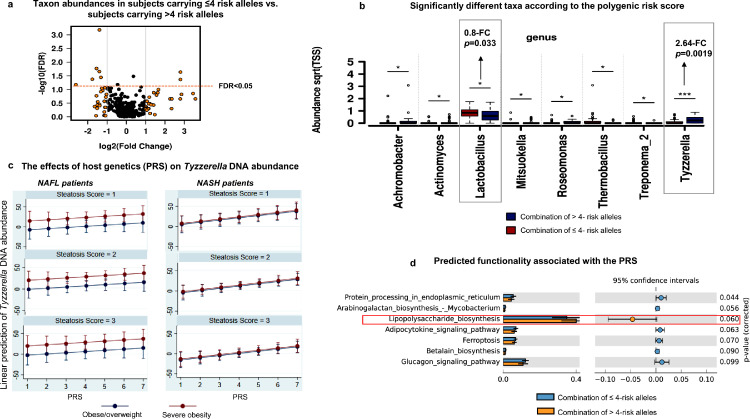
Figure 3.
Combined effect of risk alleles on the liver microbial DNA composition.
a. Volcano plot shows differentially-abundant taxa at the genus level across two groups of individuals, respectively comprising of subjects carrying ≤4 risk alleles and subjects carrying >4 risk alleles. Log2-trasnformed Genus's abundance-fold changes are shown on the X-axis (vertical lines situated at -1 and 1 indicate a 2-fold change in both directions) and the negative logarithm (base 10) of the FDR is depicted on the Y-axis (the horizontal line indicates FDR = 0.05). Black or orange dots represent genus fold changes exceeding 2 in both directions.
b. Bar chart shows significantly different taxa according to the polygenic risk score (PRS) (p < 0.05, [ANOVA]). Relative abundance is calculated as the square root of each feature read count divided by the total number of features reads in each sample. The standard error is indicated by error bars. Pair-wise comparisons are performed through t-test and are annotated as *: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, and ***: p < 0.001.
c. Plots show the effects of host genetics (PRS, the number of risk allele carried) on Tyzzerella DNA abundance [predicted by linear regression and Margins subroutine] in NAFLD patients with steatosis scores in the 1−3 range, comparing those who are overweight/moderately obese vs. severely obese patients and after adjusting for confounding factors (age and gender, in addition to steatosis score and obesity degree); the analysis was performed in patients stratified by liver disease severity, separately (NAFL in the left panels vs. NASH in the right panels).
d. Predicted functionality associated with the PRS. The functional inference was explored based on KEGG KO pathways by applying the Piphillin metagenomics inference tool35. Bars indicate mean proportions (%), confidence intervals, and their associated p-values for the top-ranked metabolic pathways corresponding to both groups with 4 ≥ PRS > 4. STAMP was used to determine differentially enriched metabolic pathways (corrected p < 0.05) and their effect sizes (η2). The Welch's test was performed to assess statistical significance and corrected p values were calculated using Storey's FDR approach.