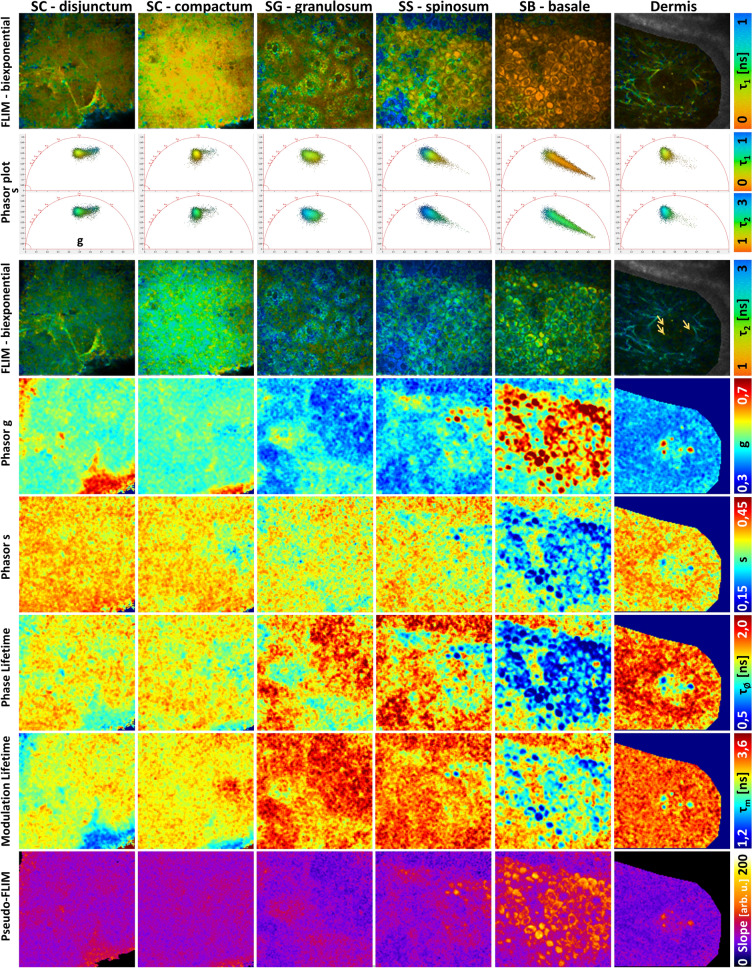
Figure 4.
Comparison of FLIM bi-exponential fitting, Phasor and Pseudo-FLIM methods for melanin detection in vivo on human skin. Multiphoton 2D 2PEF FLIM images acquired at different depths from the skin surface to the dermis, within stratum cornuem (SC) disjunctum, corneum compactum, granulosum (SG), spinosum (SS), basale (SB) and superficial dermis were analyzed with the three methods. (top) FLIM bi-exponential fitting analysis images of the short τ1 and long τ2 fluorescence lifetime parameters. (middle) Phasor analysis images of g, s, phase lifetime and modulation lifetime parameters. The corresponding phasor plots (s versus g scatters) of the different skin layers are inserted in between the τ1 and τ2 images and color coded using the same color scale as for τ1 and τ2 parameters. An enlarge view is shown in Fig. S2. (bottom) Pseudo-FLIM analysis images of the slope parameter highlighting pixels with a fast decay. The arrows indicate the fast decay pixels within the blood capillary.