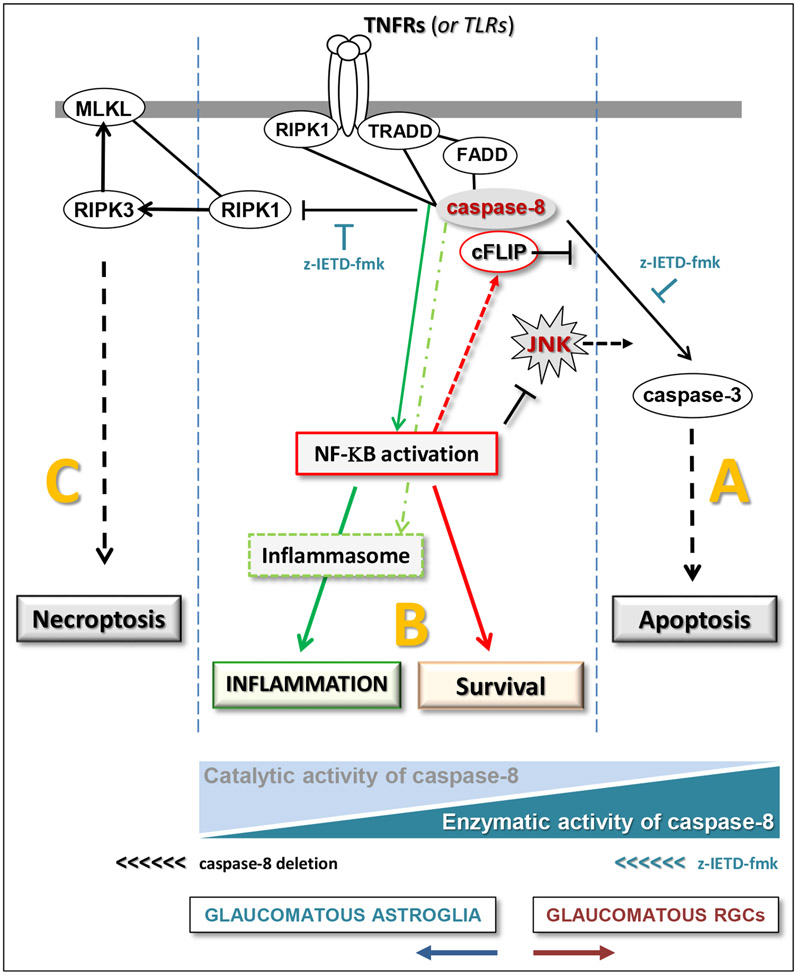
Figure 9. Molecular regulation of the parallel pathways modulating inflammation signaling.
As illustrated by the blue triangles at the bottom, different states of caspase-8 function, including its enzymatic or catalytic activities, are critical for the outcome. While the enzymatic activity of caspase-8 induces apoptosis in RGCs (A), its catalytic activity, in the absence of full proteolytic cleavage, signals towards cell survival in astroglia (B). Alternatively, the lack of caspase-8 activity induces necroptosis (C). Caspase-8 deletion in astroglia changes the state from “B to C”, while the inhibition of caspase-8 cleavage by z-IETD-fmk shifts the signal from “A to B” in RGCs. By interacting with caspase-8, cFLIP inhibits caspase-8-mediated cell death but induces pro-inflammatory outcomes. This regulator molecule that is highly expressed in astroglia but not in RGCs functions as a molecular switch between cell death, survival, and inflammation signals. This work has recently been published (Yang et al., 2021).