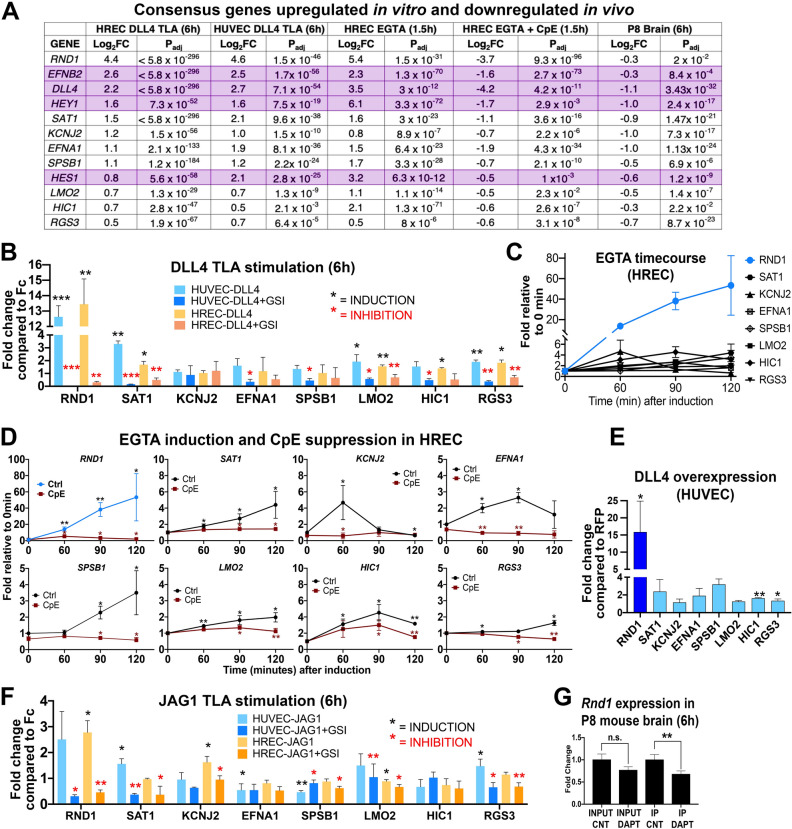
Figure 2.
RND1 is the most highly regulated of the novel Notch targets in multiple contexts. (A) 12 genes were significantly regulated under all in vitro and in vivo RNA-seq screening conditions. Genes in purple are established Notch targets. (B) qPCR confirms that 7 of the 8 novel genes are regulated by DLL4 TLA in HUVEC and HREC, with RND1 showing the highest fold induction and the strongest inhibition by CpE. Black stars indicate significant induction by DLL4, red stars indicate significant inhibition of induction by CpE. (C) All novel targets are induced by EGTA; the most strongly induced gene is RND1 (blue line). (D) EGTA induction (blue or black lines) and CpE inhibition of EGTA (red lines) of the 8 novel putative endothelial Notch targets in HREC. Black stars indicate significant induction, red stars indicate significant inhibition of induction. The y axes are scaled for each gene to visualize induction of different magnitudes. (E) RND1, HIC1, and RGS3 remain induced after 48 h of DLL4 overexpression, while the other novel targets have transient expression that has returned to baseline after 48 h. (F) JAG1 TLA induces expression of most novel endothelial Notch targets at lower levels, suggesting that RND1 is a target of both DLL4 and JAG1 signaling. (G) qPCR of endothelial transcripts immunoprecipitated from the P8 mouse brain using an endothelial-specific RiboTag allele. Input = bulk brain homogenate, IP = immunoprecipitated endothelial mRNA.