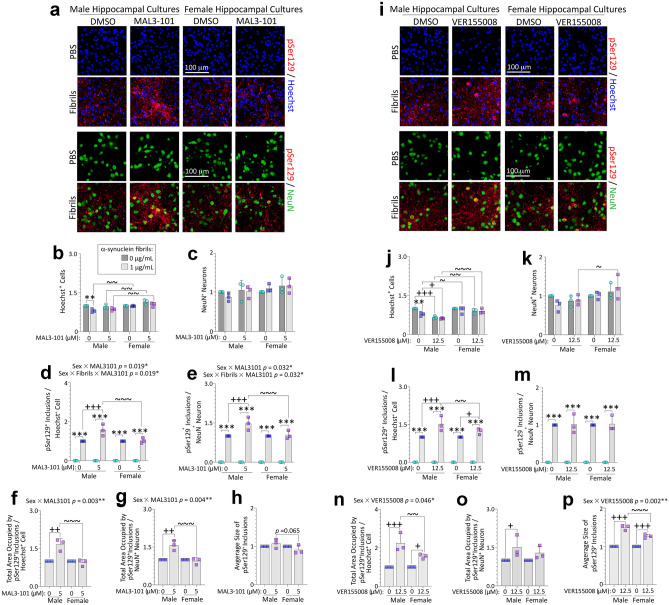
Fig. 3.
Suppression of Hsp70 function with two mechanistically independent inhibitors exacerbates α-synucleinopathy in male hippocampal cultures. Primary hippocampal cultures harvested from male vs. female rat pups were exposed to 1 μg/mL α-synuclein fibrils for 10 days. In parallel, cells were also exposed to two independent inhibitors of endogenous Hsp70 function, MAL3-101 (5 µM; a–h) or VER155008 (12.5 µM; i–p). a, i Representative photomontage of pSer129+ inclusions, NeuN+ neurons, and Hoechst-stained nuclei corresponding to quantification in b–h or j–p. Quantification of numbers of Hoechst+ cells (b, j) and NeuN+ neurons (c, k). Numbers of pSer129+ inclusions expressed as a fraction of Hoechst+ cell numbers (d, l) or NeuN+ neuron numbers (e, m). Total area occupied by the inclusions, represented as a fraction of Hoechst+ cell numbers (f, n) or NeuN+ neuronal numbers (g, o). Average size of the inclusions is shown in h and p. Shown are the mean + SD of 3 independent experiments, each performed in triplicate wells. Significant intervariable statistical interactions are shown above graphs in d–g and n, p. ** p ≤ 0.01, *** p ≤ 0.001 for 0 vs. 1 μg/mL α-synuclein fibrils; + p ≤ 0.05, + + p ≤ 0.01, + + + p ≤ 0.001 for vehicle vs Hsp70 inhibitor; ~ p ≤ 0.05, ~ ~ p ≤ 0.01, ~ ~ ~ p ≤ 0.001 for male vs. female, two or three-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc