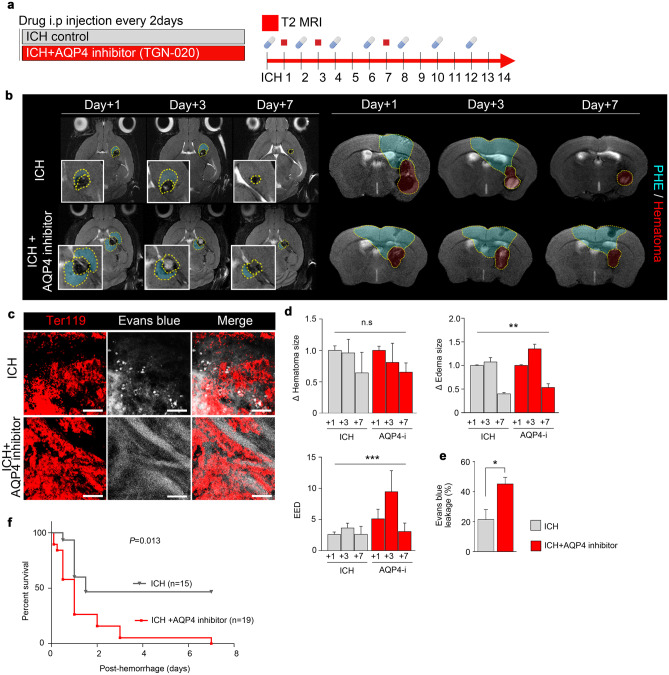
Fig. 3.
Inhibition of AQP4 worsens survival outcomes by exacerbating PHE and slowing the resolution of intracerebral hemorrhage. a AQP4 inhibitor TGN-020 (100 mg/kg) was administered in animal models of intracerebral hemorrhage. b MR images taken at 1, 3, and 7 days after intracerebral hemorrhage in mice treated with or without AQP4 inhibitor. c Immunofluorescence staining of Ter119 + red blood cells and Evans blue leakage (magnification, × 20). d, e Quantification of the changes in the sizes of hematoma, edema, relative PHE in T2WI of MRI and Evans blue leakage in confocal microscopy of PHE. f Kaplan–Meier survival curves of mice treated with or without AQP4 inhibitor after intracerebral hemorrhage. Data are mean ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001