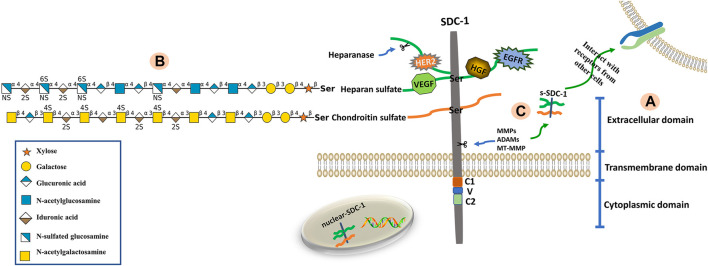
FIGURE 1.
Structure of SDC-1. (A) The SDC-1 core protein consists of three major (extracellular, transmembrane and cytoplasmic) domains. (B) The extracellular domain is bound via glycosaminoglycan (heparan sulfate, HS; chondroitin sulfate, CS) chains. The HS and CS chains are composed of repeating disaccharide units (glycan structures are represented according to the Symbol Nomenclature for Glycans (SNFG) (Cheng et al., 2017)) linked to core protein serine residues. Growth factors and receptors (e.g., HER2, VEGF, HGF and EGFR) bind to HS chains, which can be fragmented by heparanase. (C) The extracellular domain of SDC-1 is cleaved by sheddases (e.g., MMPs, ADAMs, MT-MMP), a phenomenon known as shedding. This results in the release of attached glycosaminoglycan chains as well as any bound ligands from the cell surface into the extracellular environment.