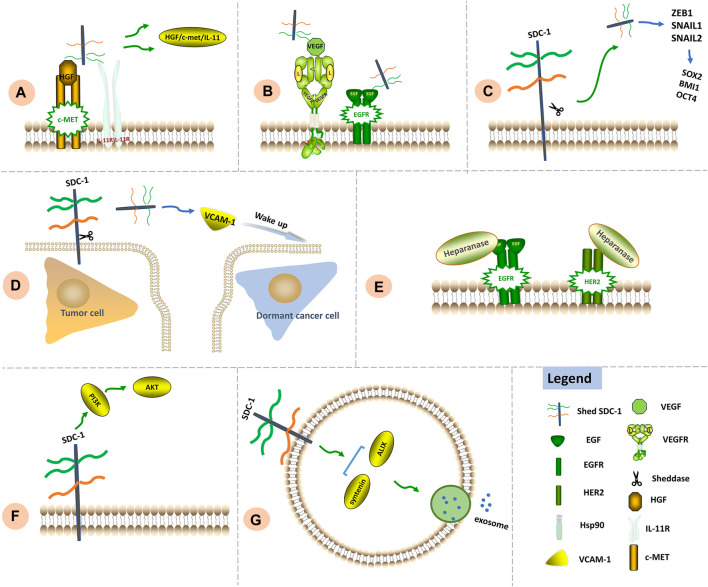
FIGURE 3.
Signaling functions of SDC-1 in chemoresistance. (A) Chemotherapy leads to SDC-1 shedding. Shed SDC-1 binds HGF/c-Met/IL-11, exacerbating drug resistance. (B) Shed SDC-1 promotes VEGF signaling. The HS chains of shed and full-length SDC-1 compete to bind downstream EGFR, thereby increasing the rate of angiogenesis as well as chemoresistance. (C) Shed SDC-1 upregulates EMT-TFs including ZEB1, Snail1 and Snail2 to induce expression of the stemness factors SOX2, BMI1 and OCT4, thus facilitating chemoresistance. (D) Shed SDC-1 increases VCAM-1 expression and subsequently promotes growth of otherwise dormant cancer cells, thus facilitating disease relapse and metastasis. (E) Increased heparanase activity contributes to lapatinib resistance via regulation of HER2 and EGFR signaling. (F) The modulation of PI3K/AKT signaling by SDC-1 has been associated with chemoresistance. (G) The SDC-1 cytoplasmic region binds syntenin and ALIX to generate a complex that allows intraluminal vesicles to emerge within endosomal membranes, thus facilitating exosome formation.