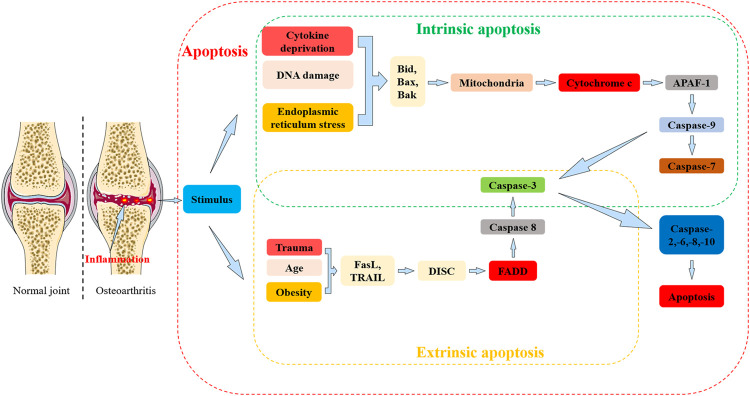
FIGURE 3.
The relationship between apoptosis and osteoarthritis (OA). Apoptosis: Apoptosis is can be divided into extrinsic and intrinsic pathways. In the extrinsic pathway, death receptors (including Fas, TRAIL) are activated and bind to corresponding ligands (including FasL) in response to stimulation by risk factors for OA (including trauma, age, obesity, etc.) to form a multi-protein complex, also known as the DISC. Activation of Caspase-8 is mediated by FADD, and Caspase-8 further activates Caspase-3 to propagate apoptotic signals. In the intrinsic pathway, intracellular damage, DNA damage and endoplasmic reticulum stress lead to activation mainly in the mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum BCL2 protein family members (including Bid, Bax, and Bak). Bcl2 protein family members can activate cytochrome c which can further activate apoptosis protease activating factor-1 (APAF-1) and caspase-9. Activated caspase-9 further activates caspases-3 and -7 which in turn activate caspases-2,-6,-8,-10 to create a positive feedback loop that amplifies the apoptotic signal and induces apoptosis.