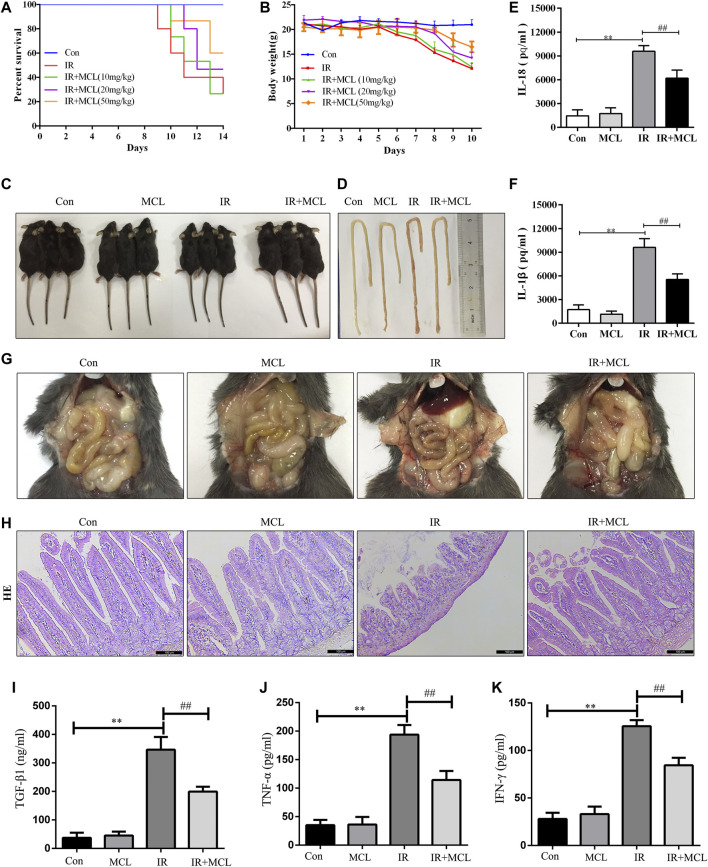
FIGURE 2.
Micheliolide (MCL) attenuates radiation-induced intestinal toxicity and inflammatory responses in wild-type (WT) mice (A) Survival curves of all experimental groups following radiation (B) Weight loss following radiation exposure (C) Representative images of mice following radiation (D, G) Representative macroscopic appearance of the small intestine following radiation with MCL treatment (E) Serum interleukin (IL)-18 levels (F) Serum IL-1β levels (I) Serum TGF-β1 levels (J) Serum TNF-α levels (K) Serum IFN-γ levels (H) Representative intestinal hematoxylin and eosin staining. Con, untreated WT mice; IL, interleukin; IR, irradiation group; MCL (10 mg/kg)+ IR, mice pre-treated with MCL (10 mg/kg) prior to irradiation; MCL (20 mg/kg)+ IR, mice pre-treated with MCL (20 mg/kg) prior to irradiation; MCL (50 mg/kg)+ IR, mice pre-treated with MCL (50 mg/kg) prior to irradiation; MCL + IR, mice pre-treated with MCL (50 mg/kg) prior to irradiation; and MCL, mice treated with MCL (50 mg/kg) without irradiation. N = 15/group. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001, two-tailed Student’s t-test.