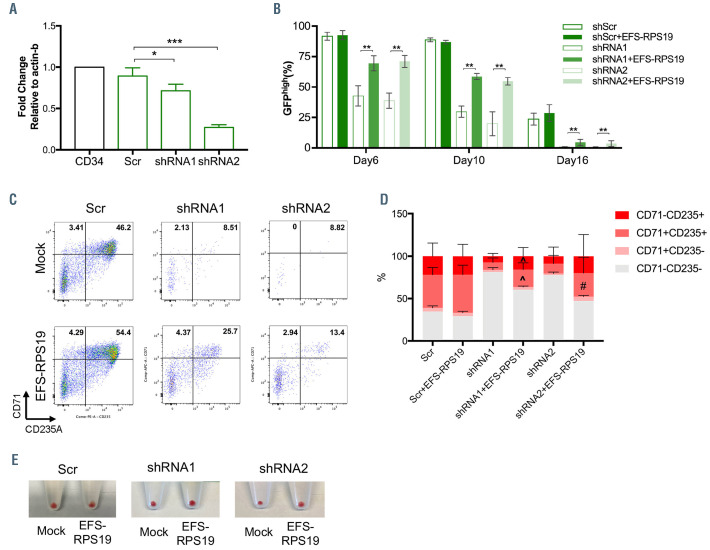
Figure 8.
Impaired erythroid differentiation of RPS19-deficient CD34+ cord blood cells can be rescued by the EFS-RPS19 vector. (A) RPS19 mRNA expression in CD34+ cord blood cells transduced with shRNA. (B) Percentage of GFPhigh population in RPS19-deficient CD34+ cord blood cells treated or not with EFS-RPS19 during erythroid differentiation from stage I to stage III. (C) Fluorescnce activated cell sorting analysis of erythroid differentiation of RPS19-deficient cells treated or not with EFS-RPS19 on day 16. (D) Percentage of indicated cell outputs of GFPhigh populations on day 16. (E) Red blood cell pellets at the end of stage III initiated with equal numbers of CD34+ cord blood cells (data shown as mean ± standard deviation, ^P<0.05 compared to the shRNA1 group, #P<0.05 compared to the shRNA2 group, *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.005 by a t-test, 3 independent experiments).