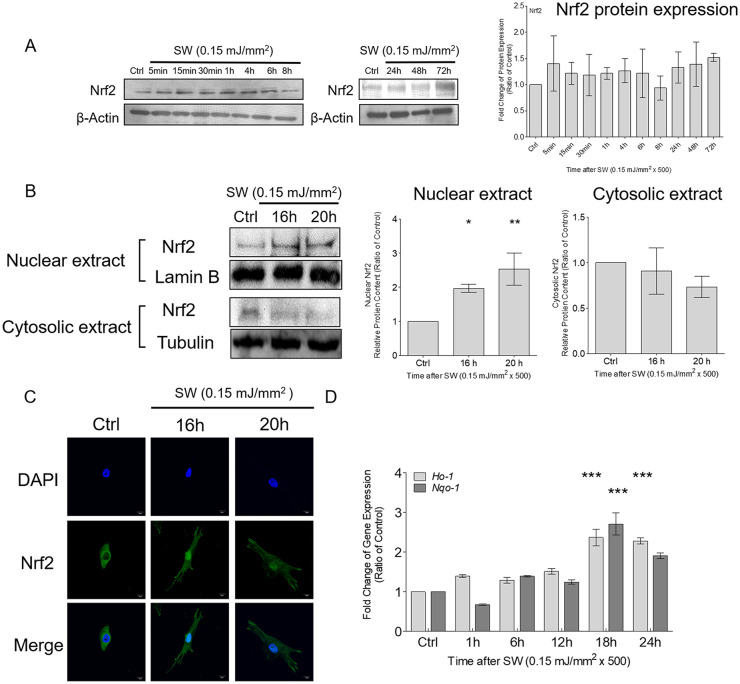
Figure 4.
Shockwave treatment increased the nuclear translocation of Nrf2 and the expression of Nrf2-dependent genes in chondrocytes. Chondrocyte pellets were treated with a single course of shockwaves (500 impulses at 0.15 mJ/mm2). (A) Times-series of the protein expression of Nrf2. (B) Nuclear translocation of Nrf2 was measured by using Western blotting. Tubulin and lamin B were used as loading controls and to specify nuclear and cytoplasmic expression, respectively. (C) The porcine articular chondrocytes were pelleted first and treated with a single course of shockwaves (500 impulses at 0.15 mJ/mm2), following which the pellets were trypsinized into separated cells and cultured in the 12-well dish for additional 16 and 20 hours. Then the immunofluorescence experiments were subsequently performed. Nuclear translocation of Nrf2 was investigated through immunofluorescence by using a specific antibody against Nrf2 and 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindolestaining for nuclei. (D) Time-series of the gene expressions of Ho-1 and Nqo-1after shockwave treatment. Each bar represents mean ± standard deviation, *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; Ctrl = control group; SW = shockwave treatment group.