Fig. 2.
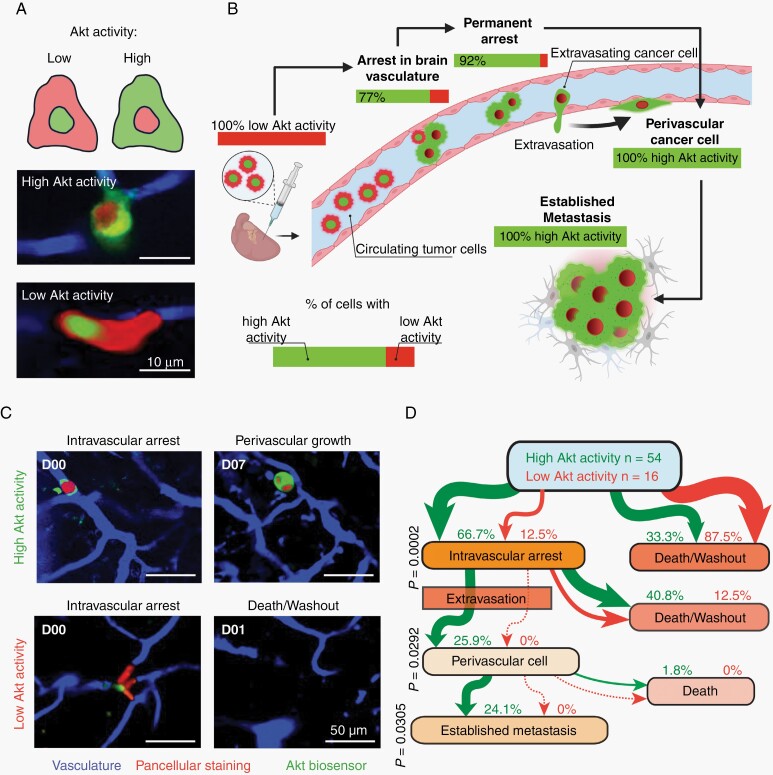
PAM pathway activation is an invariable early event in melanoma BM. (A) Intracardiac injection of biosensor labeled A2058 melanoma cells in mice for longitudinal intravital multiphoton microscopy. In vivo measurements of Akt activity on a single cell level in the brain. A2058 melanoma cells, green: Akt biosensor, red: pancellular RFP, blue: brain vessels. Scheme visualizes how to interpret fluorescent signal19. (B) Longitudinal intravital multiphoton microscopy; correlation between tumor cell’s PAM pathway activation and the steps of brain metastatic cascade is shown. A2058 cells, n = 70 tumor cells in n = 5 mice. (C, D) Within the first two hours following intracardiac injection, tumor cells can be divided into groups with high or low Akt activity. (C) Representative image shows the need for initial high Akt activity to later colonize the brain. A2058 cells, n = 70 in n = 5 mice, intravital multiphoton microscopy. (D) Flowchart demonstrates the development of BM depending on initial PAM pathway activation. Percentages refer to initially high vs low Akt activity cells in an intravascular stage. A2058 cells, n = 54/70 vs. n = 16/70 from 5 mice, Fisher’s exact test.