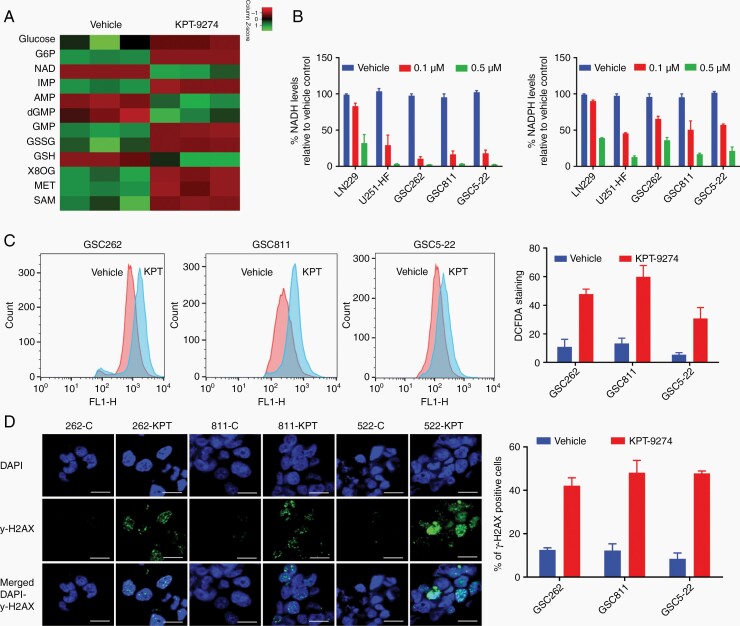
Fig. 5.
The effects of KPT-9274 on cellular metabolites and oxidative stress-dependent cell death in glioma. (A) The impact of NAMPT inhibition on NAD-related cellular metabolites assessed by a global metabolomics analysis of GSC811 cells exposed to 1 µM KPT-9274 or the vehicle. The mean peak areas from technical triplicates were compared and the fold differences were plotted as a heat map. (B) The effect of KPT-9274’s NAMPT inhibition on NADH and NADPH levels in LN229, U251-HF, GSC262, GSC811, and GSC5-22 cell lines. (C) The measurement of reactive oxygen species in GSC262, GSC811, and GSC5-22 cell lines by 2′,7′-dichlorofluorescin diacetate DCFDA staining. (D) Measurement of DNA damage by immunofluorescence assays for γ-H2AX and 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) in GSC262, GSC811, and GSC5-22 cells treated with 1µM KPT-9274 or vehicle (left panel) and the proportion of γ-H2AX-positive cells after KPT-9274 or vehicle treatment (right panel) Scale bar = 10 µm. Abbreviations: G6P, glucose 6-phosphate; NAD, nicotinamide adenine nucleotide; IMP, inosine monophosphate; AMP, adenosine monophosphate; dGMP, deoxyguanosine monophosphate; GSSG, glutathione disulfide; GSH, glutathione 8OG: 8-oxo guanosine; MET, methionine; SAM, S-adenosyl methionine.