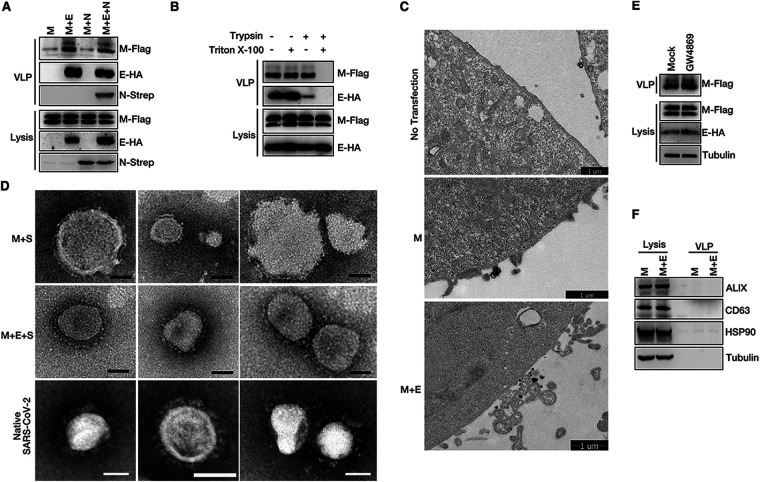
FIG 1.
SARS-CoV-2 M and E mediate VLP release. (A) M expression alone and M/E, M/N, or M/E/N coexpression in HEK293T cells. The VLP release assay was performed as described in Materials and Methods and analyzed via Western blotting (WB). (B) HEK293T cells were transfected with SARS-CoV-2 M-Flag and E-HA for 36 h. A protease protection assay of VLPs was performed as described in Materials and Methods, and then the VLPs were analyzed via WB. (C) Representative transmission electron microscopy (TEM) graphs of VLP release in no-transfection cells, cells expressing M alone, or M/E coexpression cells. (D) Representative TEM graphs of SARS-CoV-2 M and S VLPs (top), M, E, and S VLPs (middle), and native SARS-CoV-2 virions (bottom). VLP and virus samples were prepared and then visualized by TEM. Scale bar, 50 nm. (E) HEK293T cells were mock treated or treated with the exosome inhibitor GW4869, and VLP production was analyzed. (F) VLP samples with M expression alone and M/E coexpression were analyzed via WB for exosome-related proteins ALIX, CD63, and HSP90.