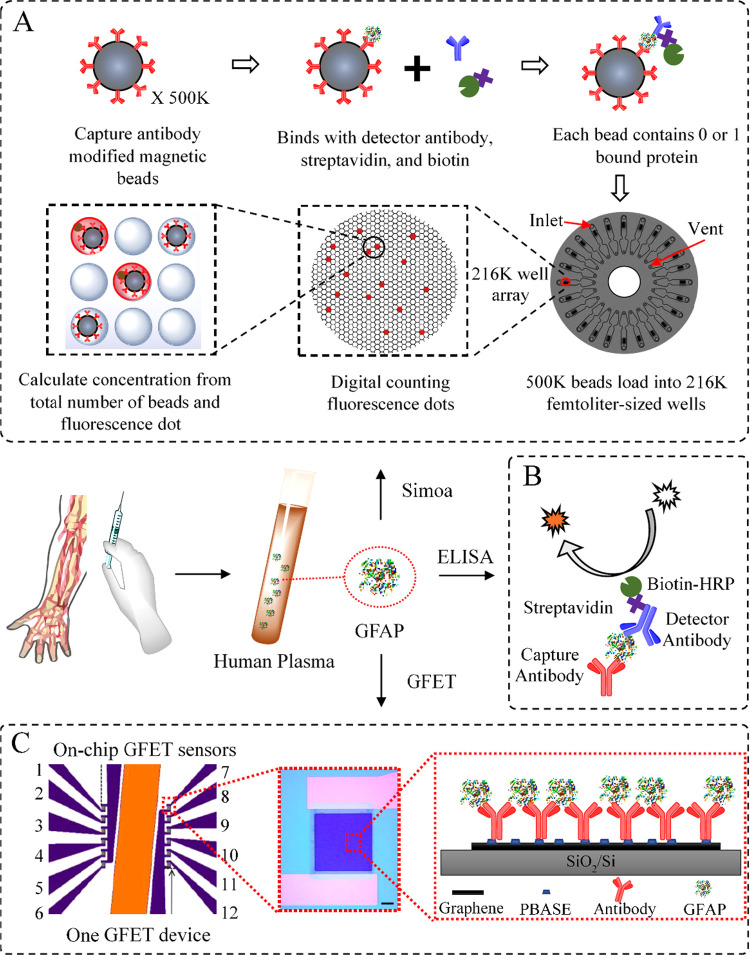
Figure 1.
Schematic of the methods for GFAP detection. (A) State-of-the-art Simoa technology relies on the effective binding between 500 K antibody-modified magnetic beads and the GFAP molecules at a low concentration. The GFAP concentration is determined by digital counting of the fluorescent signal from 216 K femtoliter-sized wells (for sample with high concentrations, there is also analogous signal quantification). (B) Classic sandwich ELISA uses an HRP-based colorimetric detection. The concentration is determined by the integration of TMB color changes. (C) On-chip GFET biosensing platform uses anti-GFAP functionalized graphene channel as a sensing element. The nonencapsulated reference electrode (orange) allows liquid gating without external electrode. Detection is based on the shift of Dirac point in response to the extent of antigen binding, which is linked to the GFAP concentration within a solution.