Figure 1.
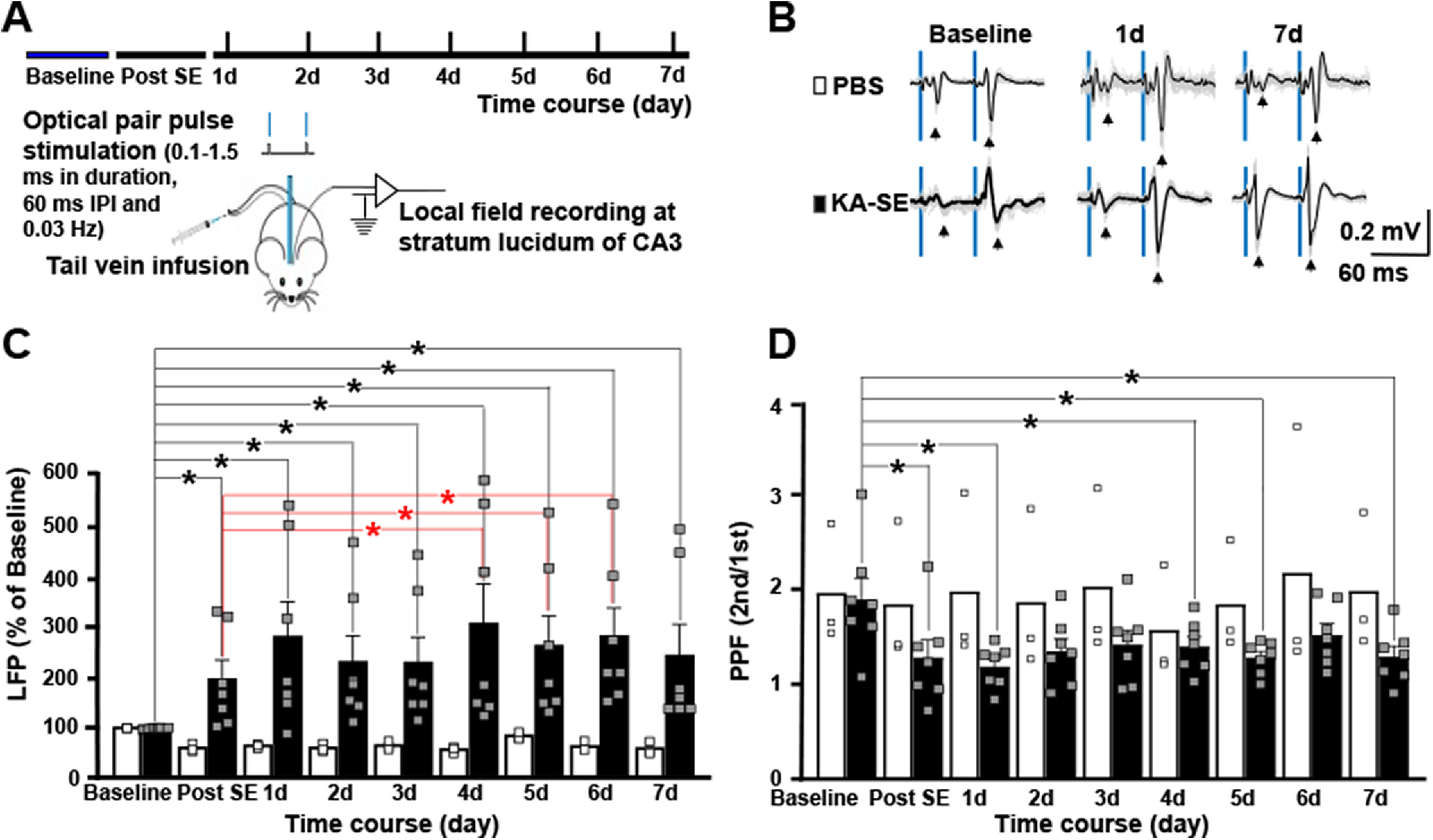
Status epilepticus induces long-lasting potentiation of mossy fiber evoked field potentials in hippocampal region CA3 in vivo. A, Schematic presents design of experiment in which optical stimulation of dentate granule cell mossy fibers evokes field potentials recorded in the ipsilateral CA3 region in awake, freely moving adult mice. Following baseline recordings collected for 2 d, animals underwent infusion of KA (16 mg/kg; n = 7) or PBS (n = 3). Field potentials evoked by pairs of optical stimuli (60-ms interval between stimuli) were recorded several hours later (“post-SE”) and at daily intervals for the following 7 d. B, Representative field potential recordings are presented for PBS and KA-treated animals at baseline, 1 and 7 d following infusion. Blue bars denote the light stimulations. Individual traces are gray and average of traces are black. C, Each of seven animals infused with KA exhibited striking increases in amplitude of evoked field potential detected several hours after status epilepticus which persisted during the following 7 d. By contrast, small reductions in the amplitude of evoked field potentials were detected in each of three animals undergoing infusion of PBS. Bars reflect the mean ± SEM; small squares reflect values of individual animals. Two-way repeated measures ANOVA with post hoc paired t tests revealed significant differences compared with baseline designated by black asterisks for both PBS and KA groups; red asterisks denote significant increases of amplitude of evoked field potentials in the KA group at days 4–6 compared with measures several hours after SE (post-SE). D, Similar statistical analyses were performed for the PPR data and significant reductions were detected at the post-SE time point in the KA group (paired t test compared with baseline p = 0.0007) as denoted by black asterisk. Although significant reductions compared with baseline in the KA group were also detected at days 1, 4, and 5 following SE, the magnitude of reduced PPRs was maximal immediately post-SE and further reductions were not observed. Apart from a reduction on day 4 (paired t test p < 0.003), no changes of PPR were detected in the PBS group.
