Figure 2.
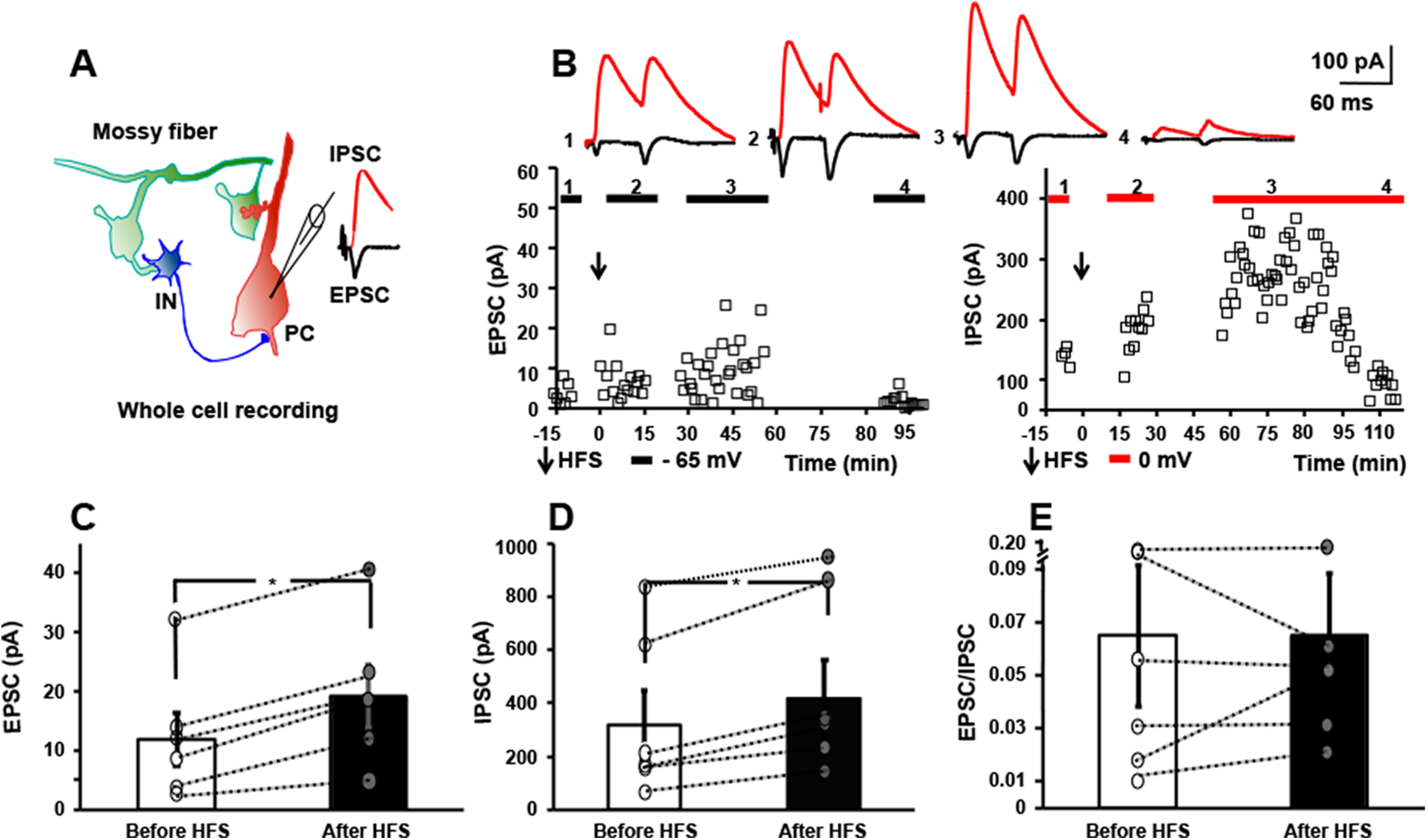
HFS of mossy fibers in vitro induces LTP of both monosynaptic EPSC and disynaptic IPSC. A, Schematic of local circuit (left) in which activation of granule cell evokes monosynaptic EPSC (black) and disynaptic IPSC (red) recorded in CA3 pyramidal cell (right). B, Responses of a CA3 pyramidal cell evoked by mossy fiber stimuli (0.033 Hz) in which EPSC (left) and IPSC (right) were collected during baseline recordings at holding potentials of −65 and 0 mv, respectively. Mossy fibers underwent HFS (denoted by arrow) at holding potential of 0 mv and EPSCs collected at holding potential of – 65 mv between 0 and 15 min and again at 30–45 min later; IPSCs were collected at holding potential of 0 mv between 15 and 30 and again between 60 and 90 min after HFS. Between 90 and 115 min, EPSCs were recorded at −65 mv and IPSCs at 0 mv in the presence of DCG-IV (1 μm). Top, Representative traces show individual EPSC and IPSC collected during baseline (1), between 0 and 30 min after HFS (2), between 30 and 90 min after HFS (3), and between 90 and 115 min after HFS in the presence of DCG-IV (1 μm). C, Results of individual cells collected before and after HFS reveal LTP of mossy fiber-CA3 EPSC (58% increase, paired t test, p = 0.006). D, Results of individual cells collected before and after HFS reveal LTP of mossy fiber-CA3 IPSC (31% increase, paired t test, p = 0.005). E, E/I ratio of the six cells before versus after HFS reveals values of 0.06 ± 0.03 before HFS, 0.06 ± 0.02 after HFS, paired t test, p = 0.5.
