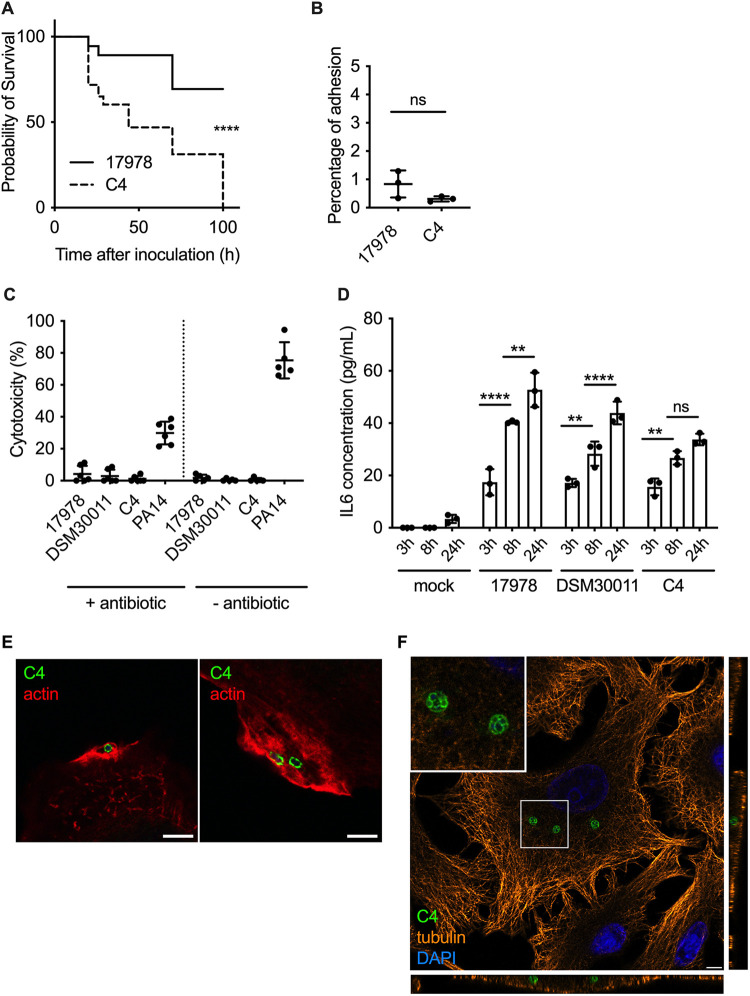
FIG 1.
Characterization of the hypervirulent A. baumannii C4 clinical strain. (A) Kaplan-Meier survival curves were generated from G. mellonella injected with the A. baumannii strains C4 or ATCC 17978 (1 × 106 CFU per insect). Mortalities were counted regularly over 100 h. A. baumannii C4 is significantly more virulent than ATCC 17978. ****, P < 0.0001 (log-rank test). Data are representative of 3 independent experiments. (B) Percentage of A. baumannii C4 and ATCC 17978 adhesion to A549 cells (MOI of 100) obtained after enumeration of viable bacteria before and after 1 h of infection. Data correspond to mean ± SD and are from 3 independent experiments. Their percentages of adhesion are not significantly different. (C) Cytotoxicity of A. baumannii ATCC 17978, DSM 30011, C4, and P. aeruginosa PA14 were monitored using LDH assay in A549 cells in the presence or absence of antibiotic. No cytotoxicity was observed for any A. baumannii strains. Data correspond to mean ± SD from 5 independent experiments. (D) Quantification of IL-6 concentration produced by A549 cells infected by A. baumannii ATCC 17978, DSM 30011, and C4 at 3 h, 8 h, and 24 hpi. Statistical comparison was done with two-way ANOVA with a Holm-Sidak’s correction for multiple comparisons. ****, P < 0.0001 between A. baumannii ATCC 17978 3 h and 8 h; **, P < 0.01 between DSM 30011 3 h and 8 h; **, P < 0.01 between C4 3 h and 8 h; **, P < 0.01 between ATCC 17978 8 h and 24 h; ****, P < 0.0001 between DSM 30011 8 h and 24 h. Not all comparisons are shown. Data correspond to mean ± SD from 3 independent experiments. (E) A549 cells were infected with A. baumannii C4, immunolabeled 1 hpi, and analyzed using confocal immunofluorescence microscopy. A. baumannii (green) was labeled with specific antibodies, and phalloidin was used to visualize actin (red). Scale bars correspond to 5 μm. (F) A549 cells were infected with A. baumannii C4 and labeled for tubulin (orange), A. baumannii (green), and the nucleus with DAPI (blue). The orthogonal view of the z-stack shows that A. baumannii C4 is able to enter into the cell and form intracellular bacterial clusters.