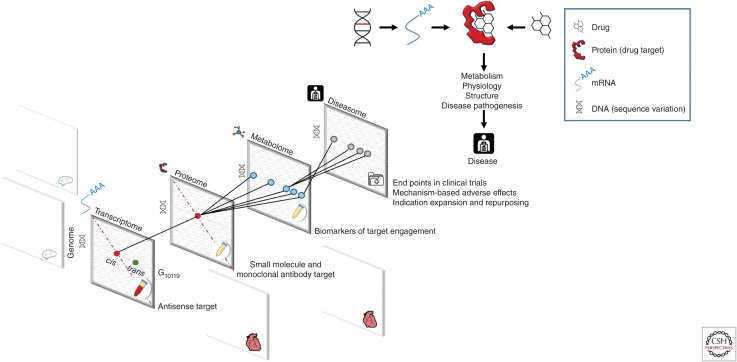
Figure 1.
Human genomics and drug development. (Right-hand panel) Relationship between human genomics and drug target identification and validation. Proteins mediate the effect of drugs and natural genetic variation on metabolism, physiology, organ structure, and disease pathogenesis. (Left-hand panel) Scalable approaches to interrogate all potential targets and diseases. Mapping the effect of genetic variation (genotype) on gene and protein expression (transcriptome and proteome) in different tissues, on metabolism (metabolome) and disease risk (diseasome), and applying drug target Mendelian randomization can help anticipate the effect of drug action on a target protein. This principle can help support drug target identification, validation, separation of “on-” from “off-target” effects, end-point selection for clinical trials and indication expansion, and repurposing priorities. Information contributing to the different data layers can be summary level and obtained in independent data sets.