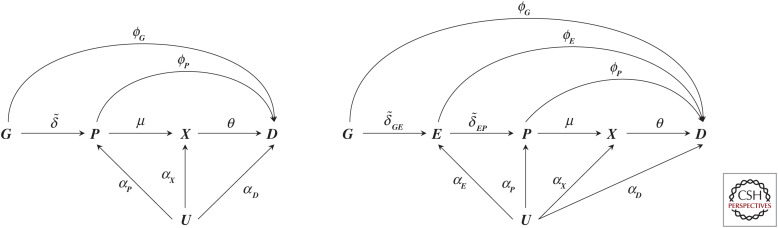
Figure 2.
A graph representation of two possible Mendelian randomization scenarios. N.B., the left-hand side of the graph represents a scenario where a single (or multiple) genetic variant is represented by node G, which has an effect (indicated by an arrow) on a protein P, where the protein affects a downstream biomarker X, and all previously defined nodes affect the outcome D. The effect magnitudes are indicated by arrow labels and may include a null effect (when there is no causal effect between two nodes). The right-hand side adds a node E, between G and P, reflecting the effect of mRNA expression on P and D. Finally, in both scenarios, all nodes except G may be affect by confounding, encoded by common cause U; of course, this node most often reflects multiple distinct causes. (Figure reprinted from Schmidt et al. 2020, courtesy of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.)