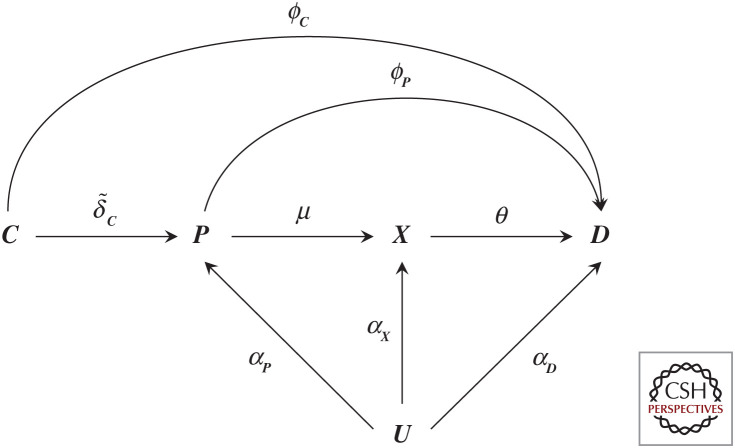
Figure 3.
A graph representation of a randomized controlled drug trial. N.B., Node C represents a randomly allocated drug compound that has an effect (indicated by an arrow) on a protein P, where the protein affects a downstream biomarker X, and all previously defined nodes affect the outcome D. Here the effect magnitudes are indicated by arrow labels and may include a null effect (when there is no causal effect between two nodes). All nodes, except C (which we assume has been allocated at random) may be affected by confounding, encoded by common cause U, where of course this node most often reflects multiple distinct causes. Finally, we note that node C is sometimes further differentiated by identifying a randomization node “Z”, which has a (strong) effect on whether one takes a drug “C” (treatment adherence), where in such a case “C” is no longer randomized and potentially affected by confounders.