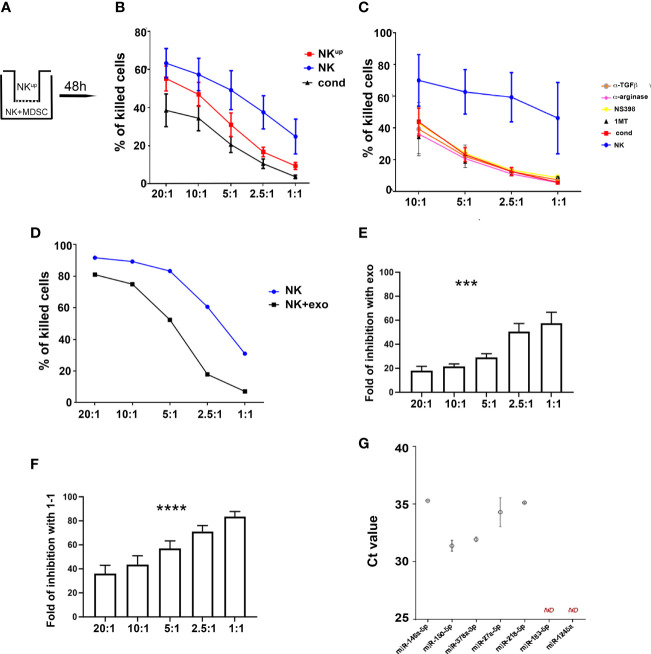
Figure 4.
PMN-MDSC-mediated inhibitory mechanisms of NK cell function. (A–C) Activated NK cells were cultured alone (NK) or with PMN-MDSC (ratio 1/1) under cell-to-cell contact or transwell (NKup) condition. After 48h of co-culture, PMN-MDSC were depleted in the 1/1 condition and the resulting NK cells were used as effector cells (cond.) in the functional assays. (A) Schematic culture conditions. (B) Percentages (mean ± SEM) of killed NALM-18 target cells at different E/T ratios in NK cells cultured alone (blue), in cell-to-cell contact with PMN-MDSC (black) and in the transwell chamber (red) (n = 6). (C) Percentages of mean ± SEM of killed NALM-18 target cells by NK cells cultured alone or in the presence of PMN-MDSC either in the absence or in the presence of indicated inhibitors and blocking mAbs (n = 3). (D) Activated NK cells were incubated with 20 ug of exo-derived PMN-MDSC. After 48h their cytolytic potential was assessed against NALM-18 cell line. Percentages of mean ± SEM of killed NALM-18 target cells at different E/T ratios. One representative experiment. (E) Fold of inhibition of NK cell killing capability upon incubation with 20ug of PMN-MDSC derived exosomes at different E/T ratios (n = 4). (F) Fold of inhibition of NK cell killing capability upon co-culturing with PMN-MDSC at different E/T ratios (n = 9). (G) Expression of immuno-modulatory miRNAs in lung cancer PMN-MDSC-derived exosomes. Real time PCR analysis for the indicated miRNAs in lung cancer PMN-MDSC exosomes. Threshold cycle (Ct) values for each miRNA are reported. Bars indicate SD (n = 2). ND, Non Detected. ***p ≤ 0.0005; ****p ≤ 0.0.00005.