Figure 3.
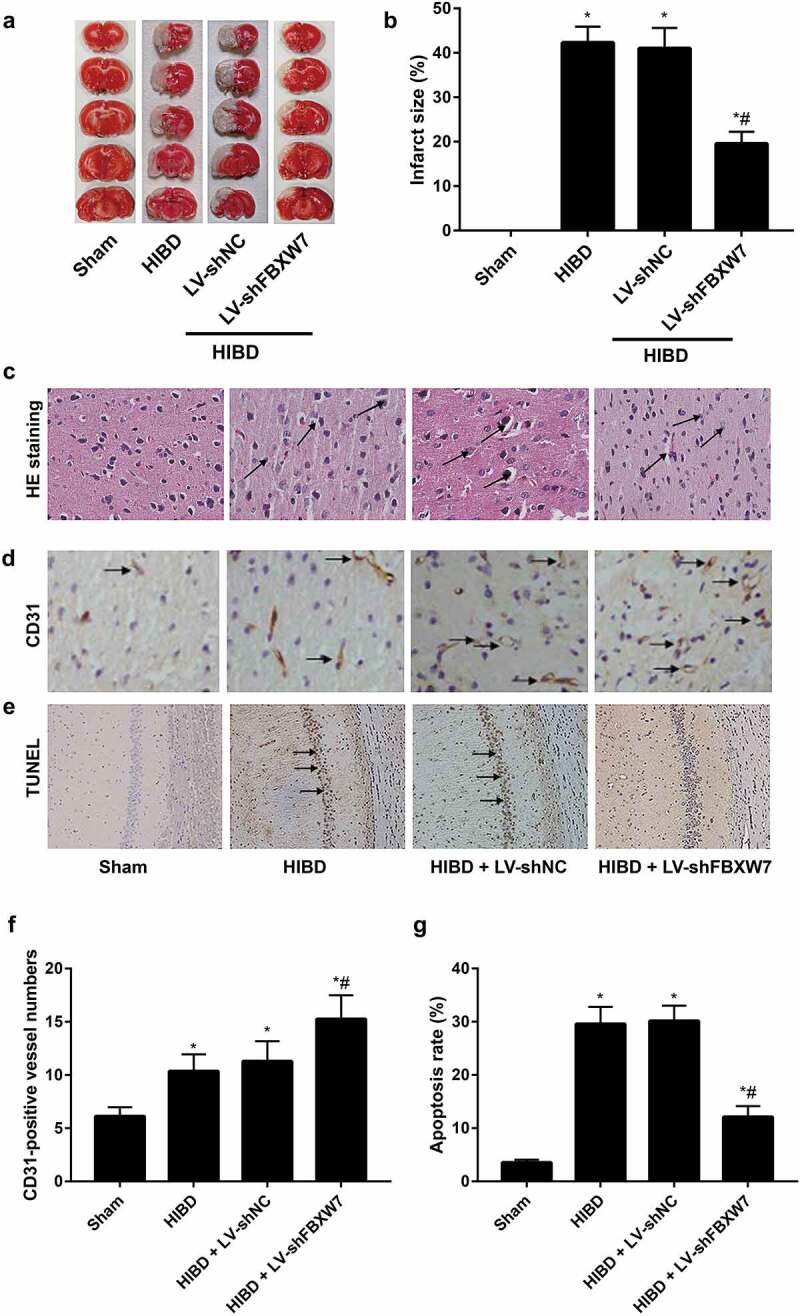
Effect of FBXW7 silencing on infarct size, angiogenesis, and apoptosis in HIBD brains
Note: a-b: Cerebral infarct size of neonatal rats in each group was evaluated using 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride (TTC) staining. c, Pathological changes in the cerebral cortex in neonatal rats were observed by hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining; black arrows indicate infiltrated inflammatory cells. d, Cerebral cortical microvessel density (MVD) was evaluated by immunohistochemical staining; black arrows indicate CD31-positive vessels. e, Terminal-deoxynucleotidyl transferase nick end labeling (TUNEL) staining of rat hippocampal sections with arrows indicating TUNEL-positive cells. f, Quantitative determination of mean CD31-positive vessel numbers of rats in each group. g, Apoptosis rate of the hippocampal CA1 region of rats in each group. All data shown are the mean ± SD (n = 6). *P < 0.05, versus sham group; #P < 0.05, versus HIBD group.
