Fig. 1.
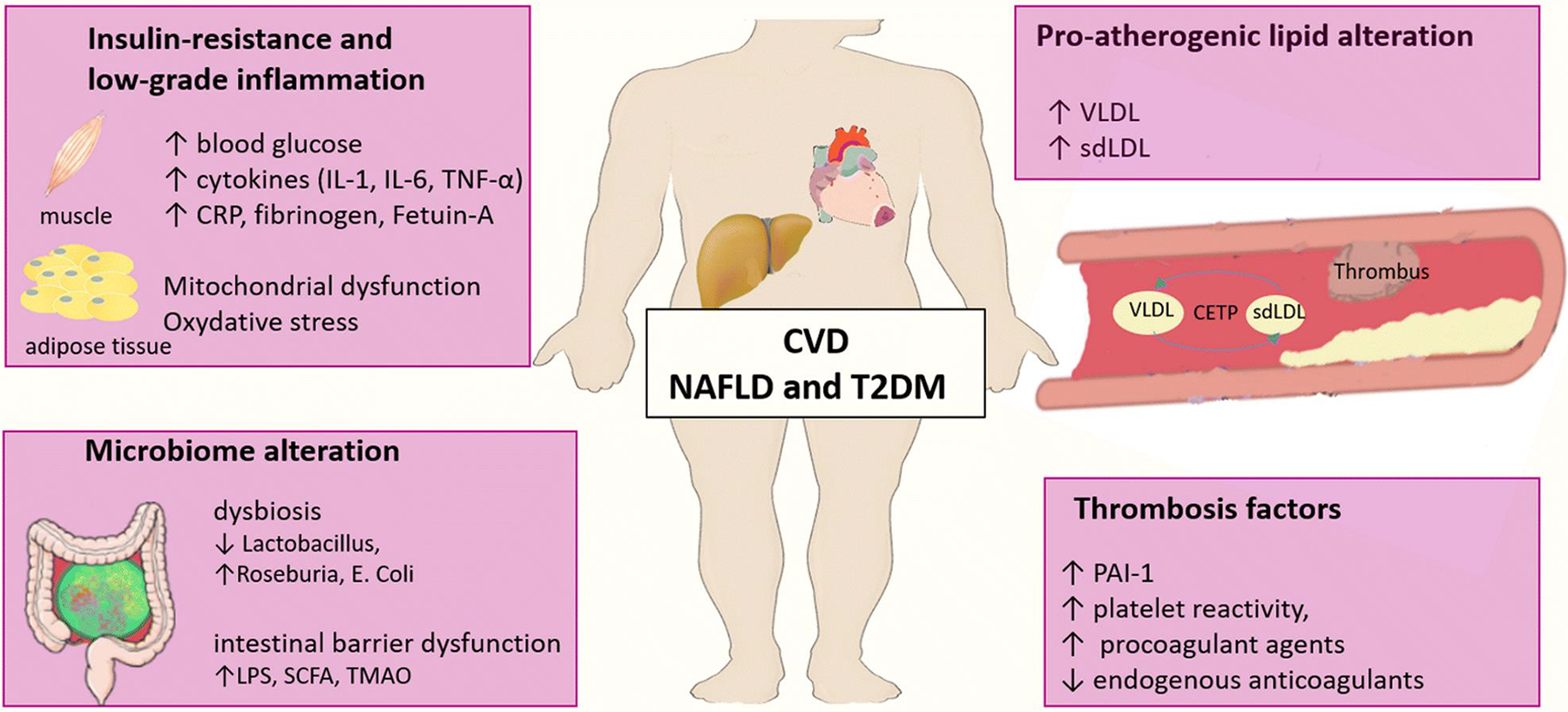
Potential pathophysiological mechanisms linking NAFLD, T2DM, and CVD. Several shared pathophysiological pathways link NAFLD and T2DM to an increased cardiovascular risk including pro-atherogenic lipid alteration, increase in thrombosis factors, insulin resistance, low-grade inflammation, and microbiome alteration.
Abbreviations: CRP: C-reactive protein, IL: interleukin, LPS: lipopolysaccharide, PAI-1: plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1, SCFA: short chain fatty acids, sdLDL: small dense low-densitylipoprotein, TMAO: trimethylamine N-oxide, TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor-α, VLDL: very low density lipoprotein
