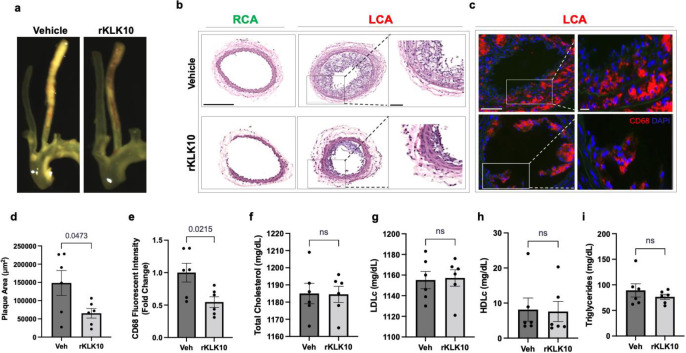
Figure 5. Treatment with rKLK10 inhibits atherosclerosis development in Apoe−/− mice.
(a) Apoe−/− were subjected to partial carotid ligation and high-fat diet feeding. The mice received either rKLK10 (0.6 mg/kg) or vehicle injection every 3 days for the duration of 3 weeks. Left carotid artery (LCA) showed plaque development, which was reduced by rKLK10 as shown by dissection microscopy. Frozen sections from the LCA and right carotid artery (RCA) were stained with (b) H&E and (c) for CD68 in LCA. DAPI (blue). Scale bar low mag = 250 μm, high mag = 50 μm. (d) Plaque area was quantified from H&E staining and is represented as μm2. (e) CD68 fluorescence intensity was quantified and is represented as the CD68 fold-change normalized to the control. Plasma lipid analysis of (f) total cholesterol, (g) low-density lipoprotein (LDL cholesterol), (h) high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, or (i) triglycerides showed no effect of rKLK10 compared to control. All data are represented as mean ± standard error of mean (SEM). Statistical analyses were performed using paired t-test. N = 6. ns = not significant.