Figure 1.
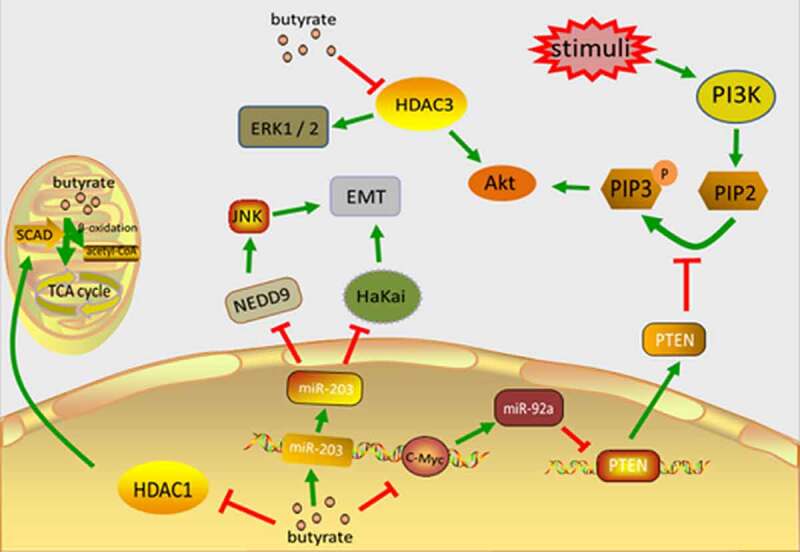
The main mechanism of butyrate inhibiting the occurrence and development of CRC. Butyrate directly enters the cell nucleus to inhibit HDAC1, reduces SCAD level, and reduces the self-oxidation of butyrate in carcinoma cells. Butyrate accumulates in cancer cells and inhibits their proliferation. Butyrate can block the activation of HDAC3, leading to decreased phosphorylation of Akt1 and erk1/2, thereby inhibiting cell motility and ultimately CRC cell migration and invasion. Butyric acid regulates the expression of c-Myc, inhibits the transcription of miR-92a, increases the expression of PTEN, and therefore antagonizes the effect of PI3K, thereby reducing the proliferation of colon cancer cells and stimulating apoptosis. Butyrate upregulates miR-203 which directly targets HaKai, reducing its level and inhibiting cell proliferation
