Figure 2.
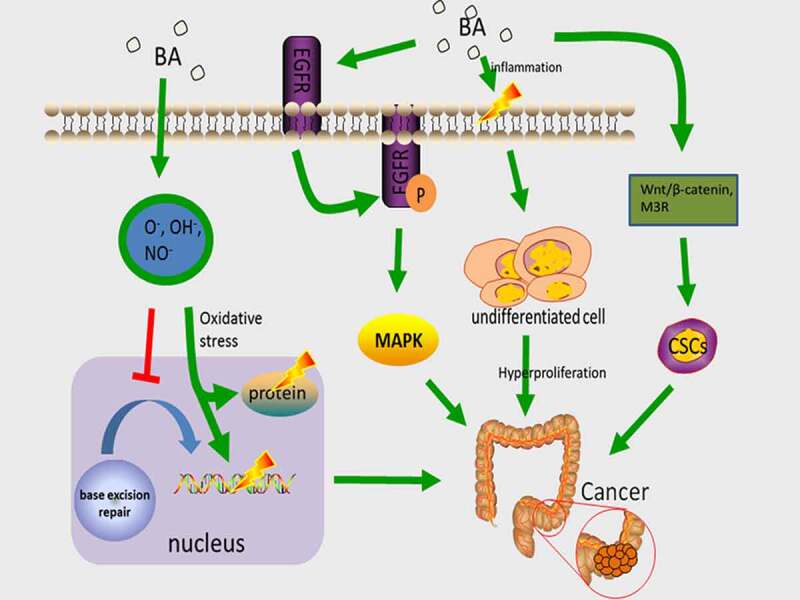
The main mechanism of BA carcinogenesis. Hydrophobic bile acids produce ROS and RNS, damage DNA and proteins, and damage BER, increasing the incidence of mutations. DCA induces PA co-localization with ERGF, promoting EGFR dimerization/multimerization and activating the MAPK cascade. activation of MAPK triggers colonic mucosal hyperproliferation, causing the development of colorectal tumors. Bile acids regulate M3R and Wnt/beta-catenin signaling and induce CSC in colonic epithelial cells, thereby inducing colon carcinogenesis
